The Caenorhabditis elegans maternal-effect sterile proteins, MES-2, MES-3, and MES-6, are associated in a complex in embryos
- PMID: 11320248
- PMCID: PMC33163
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.081016198
The Caenorhabditis elegans maternal-effect sterile proteins, MES-2, MES-3, and MES-6, are associated in a complex in embryos
Abstract
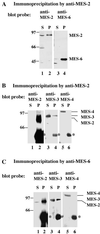
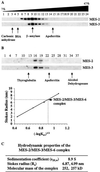
The Caenorhabditis elegans maternal-effect sterile genes, mes-2, mes-3, mes-4, and mes-6, encode nuclear proteins that are essential for germ-line development. They are thought to be involved in a common process because their mutant phenotypes are similar. MES-2 and MES-6 are homologs of Enhancer of zeste and extra sex combs, both members of the Polycomb group of chromatin regulators in insects and vertebrates. MES-3 is a novel protein, and MES-4 is a SET-domain protein. To investigate whether the MES proteins interact and likely function as a complex, we performed biochemical analyses on C. elegans embryo extracts. Results of immunoprecipitation experiments indicate that MES-2, MES-3, and MES-6 are associated in a complex and that MES-4 is not associated with this complex. Based on in vitro binding assays, MES-2 and MES-6 interact directly, via the amino terminal portion of MES-2. Sucrose density gradient fractionation and gel filtration chromatography were performed to determine the Stokes radius and sedimentation coefficient of the MES-2/MES-3/MES-6 complex. Based on those two values, we estimate that the molecular mass of the complex is approximately 255 kDa, close to the sum of the three known components. Our results suggest that the two C. elegans Polycomb group homologs (MES-2 and MES-6) associate with a novel partner (MES-3) to regulate germ-line development in C. elegans.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Polycomb group in Caenorhabditis elegans and maternal control of germline development.Development. 1998 Jul;125(13):2469-78. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.13.2469. Development. 1998. PMID: 9609830
-
Regulation of the different chromatin states of autosomes and X chromosomes in the germ line of C. elegans.Science. 2002 Jun 21;296(5576):2235-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1070790. Science. 2002. PMID: 12077420 Free PMC article.
-
MES-2, a maternal protein essential for viability of the germline in Caenorhabditis elegans, is homologous to a Drosophila Polycomb group protein.Development. 1998 Jul;125(13):2457-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.13.2457. Development. 1998. PMID: 9609829
-
Silence in the germ.Cell. 2002 Sep 20;110(6):661-4. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00967-4. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12297039 Review.
-
Preparing 2-D protein extracts from Caenorhabditis elegans.Methods Mol Biol. 1999;112:43-8. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-584-7:43. Methods Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10027227 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Removal of Polycomb repressive complex 2 makes C. elegans germ cells susceptible to direct conversion into specific somatic cell types.Cell Rep. 2012 Nov 29;2(5):1178-86. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.09.020. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23103163 Free PMC article.
-
MES-4: an autosome-associated histone methyltransferase that participates in silencing the X chromosomes in the C. elegans germ line.Development. 2006 Oct;133(19):3907-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.02584. Development. 2006. PMID: 16968818 Free PMC article.
-
The PGL family proteins associate with germ granules and function redundantly in Caenorhabditis elegans germline development.Genetics. 2004 Jun;167(2):645-61. doi: 10.1534/genetics.103.023093. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15238518 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting dosage compensation complex binding to the X chromosomes by H2A.Z/HTZ-1.PLoS Genet. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000699. Epub 2009 Oct 23. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19851459 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the X chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Mar 1;6(3):a018366. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018366. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 24591522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

