BRS1, a serine carboxypeptidase, regulates BRI1 signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 11320207
- PMCID: PMC33313
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.091065998
BRS1, a serine carboxypeptidase, regulates BRI1 signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
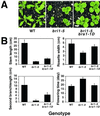
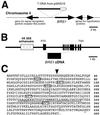
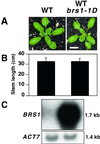
Brassinosteroid-insensitive 1 (BRI1) of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a cell surface receptor for brassinosteroids. Mutations in BRI1 severely affect plant growth and development. Activation tagging of a weak bri1 allele (bri1-5) resulted in the identification of a new locus, brs1-1D. BRS1 is predicted to encode a secreted carboxypeptidase. Whereas a brs1 loss-of-function allele has no obvious mutant phenotype, overexpression of BRS1 can suppress bri1 extracellular domain mutants. Genetic analyses showed that brassinosteroids and a functional BRI1 protein kinase domain are required for suppression. In addition, overexpressed BRS1 missense mutants, predicted to abolish BRS1 protease activity, failed to suppress bri1-5. Finally, the effects of BRS1 are selective: overexpression in either wild-type or two other receptor kinase mutants resulted in no phenotypic alterations. These results strongly suggest that BRS1 processes a protein involved in an early event in the BRI1 signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis BRS1 is a secreted and active serine carboxypeptidase.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35554-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503299200. Epub 2005 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16123046
-
BRS1 Function in Facilitating Lateral Root Emergence in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 18;18(7):1549. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071549. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28718794 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide expression and network analyses of mutants in key brassinosteroid signaling genes.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jun 22;22(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07778-w. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34157989 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand perception, activation, and early signaling of plant steroid receptor brassinosteroid insensitive 1.J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Dec;55(12):1198-211. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12081. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23718739 Review.
-
Computational modelling of the BRI1 receptor system.Plant Cell Environ. 2013 Sep;36(9):1728-37. doi: 10.1111/pce.12077. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Plant Cell Environ. 2013. PMID: 23421559 Review.
Cited by
-
Fine mapping of the reduced height gene Rht22 in tetraploid wheat landrace Jianyangailanmai (Triticum turgidum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Oct;135(10):3643-3660. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04207-8. Epub 2022 Sep 4. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 36057866
-
Molecular interactions between the specialist herbivore Manduca sexta (lepidoptera, sphingidae) and its natural host Nicotiana attenuata: V. microarray analysis and further characterization of large-scale changes in herbivore-induced mRNAs.Plant Physiol. 2003 Apr;131(4):1877-93. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.018176. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12692347 Free PMC article.
-
The POLARIS gene of Arabidopsis encodes a predicted peptide required for correct root growth and leaf vascular patterning.Plant Cell. 2002 Aug;14(8):1705-21. doi: 10.1105/tpc.002618. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12172017 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a rice dwarf mutant with a defect in brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol. 2002 Nov;130(3):1152-61. doi: 10.1104/pp.007179. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12427982 Free PMC article.
-
Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth.Genetics. 2002 Nov;162(3):1445-56. doi: 10.1093/genetics/162.3.1445. Genetics. 2002. PMID: 12454087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kauschmann A, Jessop A, Koncz C, Szekeres M, Willmitzer L, Altmann T. Plant J. 1996;9:701–713.
-
- Li J, Chory J. Cell. 1997;90:929–938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

