Localization of the Rsp5p ubiquitin-protein ligase at multiple sites within the endocytic pathway
- PMID: 11313482
- PMCID: PMC100278
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.10.3564-3575.2001
Localization of the Rsp5p ubiquitin-protein ligase at multiple sites within the endocytic pathway
Abstract
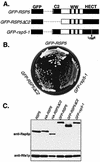
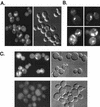
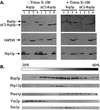
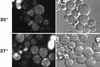
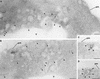
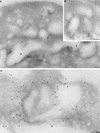
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RSP5 gene encodes an essential HECT E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. Rsp5p contains an N-terminal C2 domain, three WW domains in the central portion of the molecule, and a C-terminal catalytic HECT domain. A diverse group of substrates of Rsp5p and vertebrate C2 WW-domain-containing HECT E3s have been identified, including both nuclear and membrane-associated proteins. We determined the intracellular localization of Rsp5p and the determinants necessary for localization, in order to better understand how Rsp5p activities are coordinated. Using both green fluorescent protein fusions to Rsp5p and immunogold electron microscopy, we found that Rsp5p was distributed in a punctate pattern at the plasma membrane, corresponding to membrane invaginations that are likely sites of endosome formation, as well as at perivacuolar sites. The latter appeared to correspond to endocytic intermediates, as these structures were not seen in a sla2/end4-1 mutant, and double-immunogold labeling demonstrated colocalization of Rsp5p with the endosomal markers Pep12p and Vps32p. The C2 domain was an important determinant of localization; however, mutations that disrupted HECT domain function also caused mislocalization of Rsp5p, indicating that enzymatic activity is linked to localization. Deletion of the C2 domain partially stabilized Fur4p, a protein previously shown to undergo Rsp5p- and ubiquitin-mediated endocytosis; however, Fur4p was still ubiquitinated at the plasma membrane when the C2 domain was deleted from the protein. Together, these results indicate that Rsp5p is located at multiple sites within the endocytic pathway and suggest that Rsp5p may function at multiple steps in the ubiquitin-mediated endocytosis pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Domains of the Rsp5 ubiquitin-protein ligase required for receptor-mediated and fluid-phase endocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Feb;12(2):421-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.2.421. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11179425 Free PMC article.
-
WW domains of Rsp5p define different functions: determination of roles in fluid phase and uracil permease endocytosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2001 Jan;157(1):91-101. doi: 10.1093/genetics/157.1.91. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11139494 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin ligase Rsp5p is required for modification and sorting of membrane proteins into multivesicular bodies.Traffic. 2004 May;5(5):383-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9219.2004.00183.x. Traffic. 2004. PMID: 15086787
-
Versatile role of the yeast ubiquitin ligase Rsp5p in intracellular trafficking.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Oct;36(Pt 5):791-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0360791. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18793138 Review.
-
Ubiquitination and endocytosis of plasma membrane proteins: role of Nedd4/Rsp5p family of ubiquitin-protein ligases.J Membr Biol. 2000 Jul 1;176(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s00232001079. J Membr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10882424 Review.
Cited by
-
Gly-46 and His-50 of yeast maltose transporter Mal21p are essential for its resistance against glucose-induced degradation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jun 5;284(23):15448-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808151200. Epub 2009 Apr 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19359240 Free PMC article.
-
Ubp2 regulates Rsp5 ubiquitination activity in vivo and in vitro.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 19;8(9):e75372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075372. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24069405 Free PMC article.
-
Late assembly motifs of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 and their relative roles in particle release.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6636-48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6636-6648.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163754 Free PMC article.
-
Hse1, a component of the yeast Hrs-STAM ubiquitin-sorting complex, associates with ubiquitin peptidases and a ligase to control sorting efficiency into multivesicular bodies.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Jan;18(1):324-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-06-0557. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17079730 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding to Rsp5p regulates ubiquitination-independent vacuolar transport of Sna3p.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 May;18(5):1781-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-10-0887. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17332499 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
