Rapid signaling at inhibitory synapses in a dentate gyrus interneuron network
- PMID: 11306622
- PMCID: PMC6762544
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-08-02687.2001
Rapid signaling at inhibitory synapses in a dentate gyrus interneuron network
Abstract
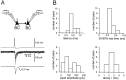
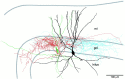
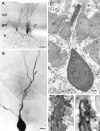
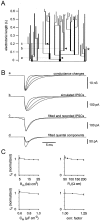
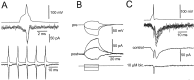
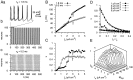
Mutual synaptic interactions between GABAergic interneurons are thought to be of critical importance for the generation of network oscillations and for temporal encoding of information in the hippocampus. However, the functional properties of synaptic transmission between hippocampal interneurons are largely unknown. We have made paired recordings from basket cells (BCs) in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices, followed by correlated light and electron microscopical analysis. Unitary GABA(A) receptor-mediated IPSCs at BC-BC synapses recorded at the soma showed a fast rise and decay, with a mean decay time constant of 2.5 +/- 0.2 msec (32 degrees C). Synaptic transmission at BC-BC synapses showed paired-pulse depression (PPD) (32 +/- 5% for 10 msec interpulse intervals) and multiple-pulse depression during repetitive stimulation. Detailed passive cable model simulations based on somatodendritic morphology and localization of synaptic contacts further indicated that the conductance change at the postsynaptic site was even faster, decaying with a mean time constant of 1.8 +/- 0.6 msec. Sequential triple recordings revealed that the decay time course of IPSCs at BC-BC synapses was approximately twofold faster than that at BC-granule cell synapses, whereas the extent of PPD was comparable. To examine the consequences of the fast postsynaptic conductance change for the generation of oscillatory activity, we developed a computational model of an interneuron network. The model showed robust oscillations at frequencies >60 Hz if the excitatory drive was sufficiently large. Thus the fast conductance change at interneuron-interneuron synapses may promote the generation of high-frequency oscillations observed in the dentate gyrus in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synaptic properties of SOM- and CCK-expressing cells in dentate gyrus interneuron networks.J Neurosci. 2014 Jun 11;34(24):8197-209. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5433-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24920624 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and stability of quantal GABA release at a hippocampal interneuron-principal neuron synapse.J Neurosci. 2000 Aug 1;20(15):5594-607. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-15-05594.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10908596 Free PMC article.
-
Use-dependent shift from inhibitory to excitatory GABAA receptor action in SP-O interneurons in the rat hippocampal CA3 area.J Neurophysiol. 2003 Sep;90(3):1983-95. doi: 10.1152/jn.00060.2003. Epub 2003 May 15. J Neurophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12750426
-
Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007 Jan;8(1):45-56. doi: 10.1038/nrn2044. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17180162 Review.
-
Inhibitory Interneurons Regulate Temporal Precision and Correlations in Cortical Circuits.Trends Neurosci. 2018 Oct;41(10):689-700. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.07.015. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Trends Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30274604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interneuronal network model of theta-nested fast oscillations predicts differential effects of heterogeneity, gap junctions and short term depression for hyperpolarizing versus shunting inhibition.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Dec 1;18(12):e1010094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010094. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36455063 Free PMC article.
-
Cell type- and input-specific differences in the number and subtypes of synaptic GABA(A) receptors in the hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2002 Apr 1;22(7):2513-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-07-02513.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11923416 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-resetting curves determine synchronization, phase locking, and clustering in networks of neural oscillators.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 22;29(16):5218-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0426-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19386918 Free PMC article.
-
Autaptic connections and synaptic depression constrain and promote gamma oscillations.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e89995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089995. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587175 Free PMC article.
-
Seizure-induced alterations in fast-spiking basket cell GABA currents modulate frequency and coherence of gamma oscillation in network simulations.Chaos. 2013 Dec;23(4):046109. doi: 10.1063/1.4830138. Chaos. 2013. PMID: 24387588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buhl EH, Halasy K, Somogyi P. Diverse sources of hippocampal unitary inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and the number of synaptic release sites. Nature. 1994;368:823–828. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G, Chrobak JJ. Temporal structure in spatially organized neuronal ensembles: a role for interneuronal networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995;5:504–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
