Structural and functional differences between two homologous mechanosensitive channels of Methanococcus jannaschii
- PMID: 11296222
- PMCID: PMC125423
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.1888
Structural and functional differences between two homologous mechanosensitive channels of Methanococcus jannaschii
Abstract
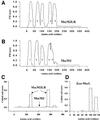
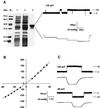
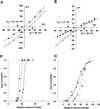
We report the molecular cloning and characterization of MscMJLR, a second type of mechanosensitive (MS) channel found in the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii. MscMJLR is structurally very similar to MscMJ, the MS channel of M.jannaschii that was identified and cloned first by using the TM1 domain of Escherichia coli MscL as a genetic probe. Although it shares 44% amino acid sequence identity and similar cation selectivity with MscMJ, MscMJLR exhibits other major functional differences. The conductance of MscMJLR of approximately 2 nS is approximately 7-fold larger than the conductance of MscMJ and rectifies with voltage. The channel requires approximately 18 kT for activation, which is three times the amount of energy required to activate MscMJ, but is comparable to the activation energy of Eco-MSCL: Our study indicates that a multiplicity of conductance-wise and energetically well-tuned MS channels in microbial cell membranes may provide for cell survival by the sequential opening of the channels upon challenge with different osmotic cues.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanosensitive channels of bacteria and archaea share a common ancestral origin.Eur Biophys J. 2002 Mar;31(1):14-25. doi: 10.1007/s002490100160. Eur Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 12046893
-
Molecular identification of a mechanosensitive channel in archaea.Biophys J. 2001 Jan;80(1):229-40. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76009-2. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11159397 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive channel of Thermoplasma, the cell wall-less archaea: cloning and molecular characterization.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2001;34(3):321-47. doi: 10.1385/CBB:34:3:321. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11898860
-
Mechanosensitive channels in archaea.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2001;34(3):349-81. doi: 10.1385/CBB:34:3:349. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11898861 Review.
-
Mechanosensitive channels in prokaryotes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2001;11(2):61-76. doi: 10.1159/000047793. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11275684 Review.
Cited by
-
MscS-like mechanosensitive channels in plants and microbes.Biochemistry. 2013 Aug 27;52(34):5708-22. doi: 10.1021/bi400804z. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23947546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Intracellular β-Barrel Residues Involved in Ion Selectivity in the Mechanosensitive Channel of Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis.Front Physiol. 2017 Oct 25;8:832. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00832. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29118717 Free PMC article.
-
Common evolutionary origins of mechanosensitive ion channels in Archaea, Bacteria and cell-walled Eukarya.Archaea. 2002 Mar;1(1):35-44. doi: 10.1155/2002/419261. Archaea. 2002. PMID: 15803657 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae MscS-Like Mechanosensitive Channel.Infect Immun. 2018 May 22;86(6):e00090-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00090-18. Print 2018 Jun. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29581189 Free PMC article.
-
Charged pore-lining residues are required for normal channel kinetics in the eukaryotic mechanosensitive ion channel MSL1.Channels (Austin). 2020 Dec;14(1):310-325. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2020.1818509. Channels (Austin). 2020. PMID: 32988273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajouz B., Berrier,C., Besnard,M., Martinac,B. and Ghazi,A. (2000) Contributions of the different extramembraneous domains of the mechanosensitive ion channel MscL to its response to membrane tension. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 1015–1022. - PubMed
-
- Barinaga M. (1994) Molecular evolution. Archaea and eukaryotes grow closer. Science, 264, 1251. - PubMed
-
- Batiza A.F., Rayment,I. and Kung,C. (1999) Channel gate! Tension, leak and disclosure. Struct. Fold. Des., 7, R99–R103. - PubMed
-
- Berrier C., Besnard,M., Ajouz,B., Coulombe,A. and Ghazi,A. (1996) Multiple mechanosensitive ion channels from Escherichia coli, activated at different thresholds of applied pressure. J. Membr. Biol., 151, 175–187. - PubMed
-
- Blount P., Sukharev,S., Moe,P., Nagle,S. and Kung,C. (1996) Towards an understanding of the structural and functional properties of MscL, a mechanosensitive channel in bacteria. Biol. Cell, 87, 1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

