X-ray structure of the human hyperplastic discs protein: an ortholog of the C-terminal domain of poly(A)-binding protein
- PMID: 11287654
- PMCID: PMC31849
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.071552198
X-ray structure of the human hyperplastic discs protein: an ortholog of the C-terminal domain of poly(A)-binding protein
Abstract
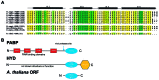
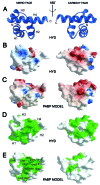
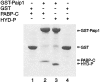
The poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) recognizes the 3' mRNA poly(A) tail and plays an essential role in eukaryotic translation initiation and mRNA stabilization/degradation. PABP is a modular protein, with four N-terminal RNA-binding domains and an extensive C terminus. The C-terminal region of PABP is essential for normal growth in yeast and has been implicated in mediating PABP homo-oligomerization and protein-protein interactions. A small, proteolytically stable, highly conserved domain has been identified within this C-terminal segment. Remarkably, this domain is also present in the hyperplastic discs protein (HYD) family of ubiquitin ligases. To better understand the function of this conserved region, an x-ray structure of the PABP-like segment of the human HYD protein has been determined at 1.04-A resolution. The conserved domain adopts a novel fold resembling a right-handed supercoil of four alpha-helices. Sequence profile searches and comparative protein structure modeling identified a small ORF from the Arabidopsis thaliana genome that encodes a structurally similar but distantly related PABP/HYD domain. Phylogenetic analysis of the experimentally determined (HYD) and homology modeled (PABP) protein surfaces revealed a conserved feature that may be responsible for binding to a PABP interacting protein, Paip1, and other shared interaction partners.
Figures

Comment in
-
Delivering messages from the 3' end.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 10;98(8):4288-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091108098. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11296278 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comparative peptide binding studies of the PABC domains from the ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligase HYD and poly(A)-binding protein. Implications for HYD function.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 19;281(20):14376-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600307200. Epub 2006 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16554297
-
Recognition of polyadenylate RNA by the poly(A)-binding protein.Cell. 1999 Sep 17;98(6):835-45. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81517-2. Cell. 1999. PMID: 10499800
-
Solution structure of the orphan PABC domain from Saccharomyces cerevisiae poly(A)-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 21;277(25):22822-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201230200. Epub 2002 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11940585
-
Regulation of poly(A)-binding protein through PABP-interacting proteins.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:537-43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.061. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381337 Review.
-
[Translational control by the poly(A) binding protein: a check for mRNA integrity].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Jul-Aug;40(4):684-93. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 16913227 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Structure of the HECT C-lobe of the UBR5 E3 ubiquitin ligase.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012 Oct 1;68(Pt 10):1158-63. doi: 10.1107/S1744309112036937. Epub 2012 Sep 22. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012. PMID: 23027739 Free PMC article.
-
Protein folding at the membrane interface, the structure of Nogo-66 requires interactions with a phosphocholine surface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 13;107(15):6847-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911817107. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20351248 Free PMC article.
-
PABP1 identified as an arginine methyltransferase substrate using high-density protein arrays.EMBO Rep. 2002 Mar;3(3):268-73. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf052. Epub 2002 Feb 15. EMBO Rep. 2002. PMID: 11850402 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Protein Synthesis in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 21;12(5):1298. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051298. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32455578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing short poly(A)-binding protein-interacting peptides for the suppression of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 22;6:37311. doi: 10.1038/srep37311. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27874031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathews M B, Sonenberg N, Hershey J W B. In: Translational Control of Gene Expression. Sonenberg N, Hershey J W B, Mathews M B, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 2000. pp. 1–32.
-
- Gingras A-C, Raught B, Sonenberg N. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:913–963. - PubMed
-
- Sachs A. In: Translational Control of Gene Expression. Sonenberg N, Hershey J W B, Mathews M B, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 2000. pp. 447–467.
-
- Hershey J W B, Merrick W C. In: Translational Control of Gene Expression. Sonenberg N, Hershey J W B, Mathews M B, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 2000. pp. 33–88.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

