Vaccine-elicited V3 loop-specific antibodies in rhesus monkeys and control of a simian-human immunodeficiency virus expressing a primary patient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate envelope
- PMID: 11287566
- PMCID: PMC114162
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.9.4165-4175.2001
Vaccine-elicited V3 loop-specific antibodies in rhesus monkeys and control of a simian-human immunodeficiency virus expressing a primary patient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate envelope
Abstract
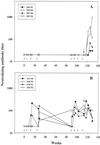
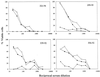
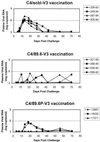
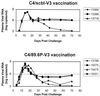
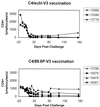
Vaccine-elicited antibodies specific for the third hypervariable domain of the surface gp120 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) (V3 loop) were assessed for their contribution to protection against infection in the simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV)/rhesus monkey model. Peptide vaccine-elicited anti-V3 loop antibody responses were examined for their ability to contain replication of SHIV-89.6, a nonpathogenic SHIV expressing a primary patient isolate HIV-1 envelope, as well as SHIV-89.6P, a pathogenic variant of that virus. Low-titer neutralizing antibodies to SHIV-89.6 that provided partial protection against viremia following SHIV-89.6 infection were generated. A similarly low-titer neutralizing antibody response to SHIV-89.6P that did not contain viremia after infection with SHIV-89.6P was generated, but a trend toward protection against CD4+ T-lymphocyte loss was seen in these infected monkeys. These observations suggest that the V3 loop on some primary patient HIV-1 isolates may be a partially effective target for neutralizing antibodies induced by peptide immunogens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vaccination of rhesus macaques with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin Env V3 elicits neutralizing antibody-mediated protection against simian-human immunodeficiency virus with a homologous but not a heterologous V3 motif.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1452-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1452-1462.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650171 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of antibodies in guinea pigs and rhesus monkeys against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope: neutralization of nonpathogenic and pathogenic primary isolate simian/human immunodeficiency virus strains.J Virol. 2000 Jan;74(1):254-63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.1.254-263.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10590113 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of immune responses induced by HIV-1 gp120 in rhesus macaques: effect of vaccination on challenge with pathogenic strains of homologous and heterologous simian human immunodeficiency viruses.Virology. 2000 Aug 15;274(1):149-64. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0444. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10936096
-
Protection of neonatal macaques against experimental SHIV infection by human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies.Transfus Clin Biol. 2001 Aug;8(4):350-8. doi: 10.1016/s1246-7820(01)00187-2. Transfus Clin Biol. 2001. PMID: 11642027 Review.
-
Polyvalent, recombinant HIV-1 virus-like particles: novel HIV-1 vaccine strategies.Antibiot Chemother (1971). 1994;46:48-61. doi: 10.1159/000423633. Antibiot Chemother (1971). 1994. PMID: 7826039 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Multigene DNA priming-boosting vaccines protect macaques from acute CD4+-T-cell depletion after simian-human immunodeficiency virus SHIV89.6P mucosal challenge.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11563-77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11563-11577.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14557642 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-clade neutralizing activity of human anti-V3 monoclonal antibodies derived from the cells of individuals infected with non-B clades of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(14):6865-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02202-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16809292 Free PMC article.
-
Nonhuman Primate Models and Understanding the Pathogenesis of HIV Infection and AIDS.ILAR J. 2017 Dec 1;58(2):160-171. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilx032. ILAR J. 2017. PMID: 29228218 Free PMC article.
-
Short Communication: Manα1-2Man-Binding Anti-HIV Lectins Enhance the Exposure of V2i and V3 Crown Neutralization Epitopes on the V1/V2 and V3 Hypervariable Loops of HIV-1 Envelope.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017 Sep;33(9):941-945. doi: 10.1089/AID.2016.0262. Epub 2017 Apr 18. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2017. PMID: 28322582 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines as adjuvants for the induction of anti-human immunodeficiency virus peptide immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA antibodies in serum and mucosal secretions after nasal immunization.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(2):517-24. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.2.517-524.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11752142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beddows S, Louisirirotchanakul S, Cheingsong-Popov R, Eastbrook P J, Simmonds P, Weber J. Neutralization of primary and T-cell line adapted isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: role of V3-specific antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1998;79:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Bures, R., A. Gaitan, T. Zhu, C. Graziosi, K. McGrath, J. Tartaglia, P. Caudrelier, R. E. L. Habib, M. Klein, A. Lazzarin, D. Stablein, M. Deers, L. Corey, M. L. Greenberg, D. H. Schwartz, and D. C. Montefiori. Immunization with recombinant canarypox vectors expressing membrane-anchored gp120 followed by gp160 protein boosting fails to generate antibodies that neutralize R5 primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses, in press. - PubMed
-
- Cheingsong-Popov R, Osmanov S, Pau C-P, Schochetman G, Barin F, Holmes H, Francis G, Ruppach H, Dietrich U, Lister S, Weber J. Serotyping of HIV-1 infections: definition, relationship to viral genetic subtypes, and assay evaluation. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998;14:311–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

