Fibroblast growth factors
- PMID: 11276432
- PMCID: PMC138918
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-3-reviews3005
Fibroblast growth factors
Abstract
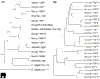
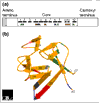
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) make up a large family of polypeptide growth factors that are found in organisms ranging from nematodes to humans. In vertebrates, the 22 members of the FGF family range in molecular mass from 17 to 34 kDa and share 13-71% amino acid identity. Between vertebrate species, FGFs are highly conserved in both gene structure and amino-acid sequence. FGFs have a high affinity for heparan sulfate proteoglycans and require heparan sulfate to activate one of four cell-surface FGF receptors. During embryonic development, FGFs have diverse roles in regulating cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. In the adult organism, FGFs are homeostatic factors and function in tissue repair and response to injury. When inappropriately expressed, some FGFs can contribute to the pathogenesis of cancer. A subset of the FGF family, expressed in adult tissue, is important for neuronal signal transduction in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signaling, internalization, and intracellular activity of fibroblast growth factor.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;286:45-79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-69494-6_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15645710 Review.
-
Common and specific determinants for fibroblast growth factors in the ectodomain of the receptor kinase complex.Biochemistry. 1999 Jan 5;38(1):160-71. doi: 10.1021/bi981758m. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 9890894
-
Fibroblast (heparin-binding) growing factors in neuronal development and repair.Mol Neurobiol. 1988 Winter;2(4):263-89. doi: 10.1007/BF02935635. Mol Neurobiol. 1988. PMID: 2855976 Review.
-
Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor bind with differing affinity to the same heparan sulfate proteoglycan on BALB/c 3T3 cells: implications for potentiation of growth factor action by heparin.J Cell Biochem. 1995 May;58(1):6-14. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240580103. J Cell Biochem. 1995. PMID: 7543903
-
FGFs, heparan sulfate and FGFRs: complex interactions essential for development.Bioessays. 2000 Feb;22(2):108-12. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(200002)22:2<108::AID-BIES2>3.0.CO;2-M. Bioessays. 2000. PMID: 10655030 Review.
Cited by
-
Production of IL-8, IL-17, IFN-gamma and IP-10 in human astrocytes correlates with alphavirus attenuation.Vet Microbiol. 2013 May 3;163(3-4):223-34. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.11.021. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23428380 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2 promotes the expansion of parietal mesothelial progenitor pools and inhibits BMP4-mediated smooth muscle cell differentiation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Sep 23;12:1387237. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1387237. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39376629 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Am J Pathol. 2021 Jul;191(7):1180-1192. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.04.014. Epub 2021 May 14. Am J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34000282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9) on steroidogenesis and gene expression and control of FGF9 mRNA in bovine granulosa cells.Endocrinology. 2012 Sep;153(9):4491-501. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1003. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22798350 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of duodenal atresias in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2IIIb-/- mouse embryos occurs in the absence of an endodermal plug.J Pediatr Surg. 2012 Jul;47(7):1369-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.02.001. J Pediatr Surg. 2012. PMID: 22813799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kiefer P, Acland P, Pappin D, Peters G, Dickson C. Competition between nuclear localization and secretory signals determines the subcellular fate of a single CUG-initiated form of FGF3. EMBO J. 1994;13:4126–4136. This is one of first papers to show that an FGF can initiate from an upstream CUG codon and can be localized in the nucleus. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnaud E, Touriol C, Boutonnet C, Gensac MC, Vagner S, Prats H, Prats AC. A new 34-kilodalton isoform of human fibroblast growth factor 2 is cap dependently synthesized by using a non-AUG start codon and behaves as a survival factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:505–514. Identification of a high-molecular-weight form of FGF2 that initiates from an upsteam CUG codon and is localized in the nucleus. - PMC - PubMed
-
- GenBank http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/index.html DNA sequences of FGFs listed in Table 1 can be accessed through this website.
-
- HUGO Gene Nomenclature Database http://www.gene.ucl.ac.uk/nomenclature/ This database contains nomenclature and mapping information for human genes.
-
- Cytokine Family cDNA Database http://cytokine.medic.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/CFC/FGF/FGF.html This database contains nomenclature and mapping information for the FGF family.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

