Expanding the genetic code: selection of efficient suppressors of four-base codons and identification of "shifty" four-base codons with a library approach in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 11273699
- PMCID: PMC7125544
- DOI: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4518
Expanding the genetic code: selection of efficient suppressors of four-base codons and identification of "shifty" four-base codons with a library approach in Escherichia coli
Abstract
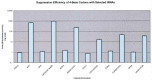
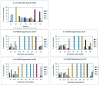
Naturally occurring tRNA mutants are known that suppress +1 frameshift mutations by means of an extended anticodon loop, and a few have been used in protein mutagenesis. In an effort to expand the number of possible ways to uniquely and efficiently encode unnatural amino acids, we have devised a general strategy to select tRNAs with the ability to suppress four-base codons from a library of tRNAs with randomized 8 or 9 nt anticodon loops. Our selectants included both known and novel suppressible four-base codons and resulted in a set of very efficient, non-cross-reactive tRNA/four-base codon pairs for AGGA, UAGA, CCCU and CUAG. The most efficient four-base codon suppressors had Watson-Crick complementary anticodons, and the sequences of the anticodon loops outside of the anticodons varied with the anticodon. Additionally, four-base codon reporter libraries were used to identify "shifty" sites at which +1 frameshifting is most favorable in the absence of suppressor tRNAs in Escherichia coli. We intend to use these tRNAs to explore the limits of unnatural polypeptide biosynthesis, both in vitro and eventually in vivo. In addition, this selection strategy is being extended to identify novel five- and six-base codon suppressors.
Copyright 2001 Academic Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the limits of codon and anticodon size.Chem Biol. 2002 Feb;9(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(02)00094-7. Chem Biol. 2002. PMID: 11880038
-
Quadruplet codons: implications for code expansion and the specification of translation step size.J Mol Biol. 2000 Apr 28;298(2):195-209. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3658. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10764591
-
In vitro codon-reading specificities of unmodified tRNA molecules with different anticodons on the sequence background of Escherichia coli tRNASer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Apr 21;257(3):662-7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0538. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10208840
-
Decoding the genome: a modified view.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jan 9;32(1):223-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh185. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14715921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
tRNA's wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification.J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 9;366(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.046. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17187822 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Site-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Synthetic Biology.Chem Rev. 2024 Sep 25;124(18):10577-10617. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00938. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39207844 Review.
-
Extensive frameshift at all AGG and CCC codons in the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene of Perkinsus marinus (Alveolata; Dinoflagellata).Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(18):6186-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq449. Epub 2010 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20507907 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling the Replication of a Genomically Recoded HIV-1 with a Functional Quadruplet Codon in Mammalian Cells.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 Jun 15;7(6):1612-1617. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00096. Epub 2018 Jun 5. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 29787233 Free PMC article.
-
High frequency of +1 programmed ribosomal frameshifting in Euplotes octocarinatus.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 19;6:21139. doi: 10.1038/srep21139. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26891713 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments of engineered translational machineries for the incorporation of non-canonical amino acids into polypeptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 20;16(3):6513-31. doi: 10.3390/ijms16036513. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25803109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atkins J.F., Weiss R.B., Thompson S., Gesteland R.F. Towards a genetic dissection of the basis of triplet decoding, and its natural subversion: programmed reading frame shifts and hops. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1991;25:201–228. - PubMed
-
- Auffinger P., Westhof E. Singly and bifurcated hydrogen-bonded base-pairs in tRNA anticodon hairpins and ribozymes. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;292:467–483. - PubMed
-
- Ayer D., Yarus M. The context effect does not require a fourth base-pair. Science. 1986;231:393–395. - PubMed
Further reading
-
- Winey M., Mendenhall M.D., Cummins C.M., Culbertson M.R., Knapp G. Splicing of a yeast proline tRNA containing a novel suppressor mutation in the anticodon stem. J. Mol. Biol. 1986;192:49–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

