The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase DDR1 in arterial wound repair
- PMID: 11254672
- PMCID: PMC208942
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10720
The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase DDR1 in arterial wound repair
Abstract
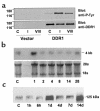
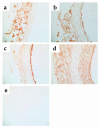
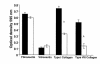
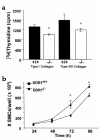
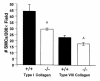
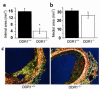
Collagens act as important signaling molecules regulating vascular smooth muscle cell responses during arterial wound repair. Discoidin domain receptors (DDRs) are a novel class of receptor tyrosine kinases that bind to several collagens and stimulate matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) production, but little is known about their expression and function in the vasculature. We posited a critical role for the DDRs controlling smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation and thus repair following arterial injury. Smooth muscle cells were isolated from the aortas of mice with a targeted deletion of the DDR1 gene (DDR1-null) and studied in culture using models that mimic critical steps in neointimal thickening. Our studies suggest that DDR1 plays an important role in regulating attachment to collagen, chemotaxis, proliferation, and MMP production in smooth muscle cells. Following mechanical injury to the carotid arteries, cross-sectional area of the neointima was significantly lower in DDR1-null mice than in wild-type mice. There was also a significant decrease in collagen deposition in the injured arteries of the DDR1-null mice. Our results support the hypothesis that DDR1 plays an important role as a collagen receptor, mediating intimal thickening after vascular injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deletion of discoidin domain receptor 2 does not affect smooth muscle cell adhesion, migration, or proliferation in response to type I collagen.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2012 May-Jun;21(3):214-8. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2011.07.006. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2012. PMID: 21865059
-
Discoidin domain receptor 1 (ddr1) deletion decreases atherosclerosis by accelerating matrix accumulation and reducing inflammation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.Circ Res. 2008 May 23;102(10):1202-11. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.170662. Epub 2008 May 1. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18451340
-
Tyrosine kinase activity of discoidin domain receptor 1 is necessary for smooth muscle cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase expression.Circ Res. 2002 Jun 14;90(11):1147-9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000022166.74073.f8. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 12065315
-
Exploring the Cellular and Molecular Mechanism of Discoidin Domain Receptors (DDR1 and DDR2) in Bone Formation, Regeneration, and Its Associated Disease Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 4;24(19):14895. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914895. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagen recognition and transmembrane signalling by discoidin domain receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23128141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ALKBH1-demethylated DNA N6-methyladenine modification triggers vascular calcification via osteogenic reprogramming in chronic kidney disease.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jul 15;131(14):e146985. doi: 10.1172/JCI146985. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34003800 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of type VIII collagen in mice ameliorates diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes. 2009 Jul;58(7):1672-81. doi: 10.2337/db08-0183. Epub 2009 Apr 28. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19401424 Free PMC article.
-
Discoidin domain receptor 2 is associated with the increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Oct;330(1-2):141-52. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0127-0. Epub 2009 May 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19415460
-
Shedding of discoidin domain receptor 1 by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):12114-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.409599. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23519472 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Discoidin Domain Receptors in Ligamentum Flavum Fibrosis in Patients with Degenerative Lumbar Canal Stenosis.Asian Spine J. 2023 Feb;17(1):194-202. doi: 10.31616/asj.2021.0380. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Asian Spine J. 2023. PMID: 36163678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strauss BH, et al. Extracellular matrix remodeling after balloon angioplasty injury in a rabbit model of restenosis. Circ Res. 1994;75:650–658. - PubMed
-
- Bendeck MP, et al. Differential expression of α1 type VIII collagen in injured, platelet-derived growth factor-BB stimulated rat carotid arteries. Circ Res. 1996;79:524–531. - PubMed
-
- Sibinga NES, et al. Collagen VIII is expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells in response to vascular injury. Circ Res. 1997;80:532–541. - PubMed
-
- Plenz G, Dorszewski A, Breithardt G, Robenek H. Expression of type VIII collagen after cholesterol diet and injury in the rabbit model of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:1201–1209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

