Activation of protein tyrosine kinases by Coxiella burnetii: role in actin cytoskeleton reorganization and bacterial phagocytosis
- PMID: 11254615
- PMCID: PMC98187
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2520-2526.2001
Activation of protein tyrosine kinases by Coxiella burnetii: role in actin cytoskeleton reorganization and bacterial phagocytosis
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern for Meconi et al., "Activation of Protein Tyrosine Kinases by Coxiella burnetii: Role in Actin Cytoskeleton Reorganization and Bacterial Phagocytosis".Infect Immun. 2023 Nov 16;91(11):e0026223. doi: 10.1128/iai.00262-23. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 37905806 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Coxiella burnetii, the agent of Q fever, is an obligate intracellular microorganism that grows in monocytes/macrophages. The internalization of virulent organisms by monocytes is lower than that of avirulent variants and is associated with actin cytoskeleton reorganization. We studied the activation of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) by C. burnetii in THP-1 monocytes. Virulent organisms induced early PTK activation and the tyrosine phosphorylation of several endogenous substrates, including Hck and Lyn, two Src-related kinases. PTK activation reflects C. burnetii virulence since avirulent variants were unable to stimulate PTK. We also investigated the role of PTK activation in C. burnetii-stimulated F-actin reorganization. Tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins were colocalized with F-actin inside cell protrusions induced by C. burnetii, and PTK activity was increased in Triton X-100-insoluble fractions. In addition, lavendustin A, a PTK inhibitor, and PP1, a Src kinase inhibitor, prevented C. burnetii-induced cell protrusions and F-actin reorganization. We finally assessed the role of PTK activation in bacterial phagocytosis. Pretreatment of THP-1 cells with lavendustin A and PP1 upregulated the uptake of virulent C. burnetii but had no effect on the phagocytosis of avirulent organisms. Thus, it is likely that PTK activation by C. burnetii negatively regulates bacterial uptake by interfering with cytoskeleton organization.
Figures
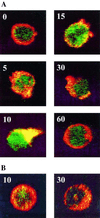
Similar articles
-
Coxiella burnetii induces reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in human monocytes.Infect Immun. 1998 Nov;66(11):5527-33. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5527-5533.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9784567 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide from Coxiella burnetii is involved in bacterial phagocytosis, filamentous actin reorganization, and inflammatory responses through Toll-like receptor 4.J Immunol. 2004 Mar 15;172(6):3695-703. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.6.3695. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15004173
-
Coxiella burnetii avoids macrophage phagocytosis by interfering with spatial distribution of complement receptor 3.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 15;170(8):4217-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4217. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12682255
-
Intracellular life of Coxiella burnetii in macrophages.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 May;1166:55-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04515.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19538264 Review.
-
"Hairiness" is a Facsimile of Reorganized Cytoskeletons: A Cytopathic Effect of Coxiella burnetii.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Oct;60(10):890-897. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.10.890. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 31538423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cortactin is involved in the entry of Coxiella burnetii into non-phagocytic cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039348. Epub 2012 Jun 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761768 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Goats in the Epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;11(12):1703. doi: 10.3390/biology11121703. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of the obligate intracellular bacterium Coxiella burnetii.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Aug;11(8):561-73. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3049. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23797173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating mechanisms underlying genetic resistance to Salmon Rickettsial Syndrome in Atlantic salmon using RNA sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2021 Mar 6;22(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07443-2. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33676414 Free PMC article.
-
Right on Q: genetics begin to unravel Coxiella burnetii host cell interactions.Future Microbiol. 2016 Jul;11(7):919-39. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0044. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Future Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27418426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Capo C, Lindberg F P, Meconi S, Zaffran Y, Tardei G, Brown E J, Raoult D, Mege J L. Subversion of monocyte functions by Coxiella burnetii: impairment of the cross-talk between αvβ3 integrin and CR3. J Immunol. 1999;163:6078–6085. - PubMed
-
- Capo C, Meconi S, Sanguedolce M V, Bardin N, Flatau G, Boquet P, Mege J L. Effect of cytotoxic necrotizing factor-1 on actin cytoskeleton: role in the regulation of integrin-dependent phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1998;161:4301–4308. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

