The nuclear export receptor Xpo1p forms distinct complexes with NES transport substrates and the yeast Ran binding protein 1 (Yrb1p)
- PMID: 11251069
- PMCID: PMC30962
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.3.539
The nuclear export receptor Xpo1p forms distinct complexes with NES transport substrates and the yeast Ran binding protein 1 (Yrb1p)
Abstract
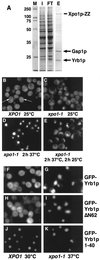
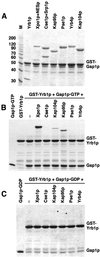
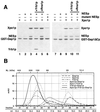
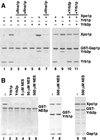
Xpo1p (Crm1p) is the nuclear export receptor for proteins containing a leucine-rich nuclear export signal (NES). Xpo1p, the NES-containing protein, and GTP-bound Ran form a complex in the nucleus that translocates across the nuclear pore. We have identified Yrb1p as the major Xpo1p-binding protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae extracts in the presence of GTP-bound Gsp1p (yeast Ran). Yrb1p is cytoplasmic at steady-state but shuttles continuously between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Nuclear import of Yrb1p is mediated by two separate nuclear targeting signals. Export from the nucleus requires Xpo1p, but Yrb1p does not contain a leucine-rich NES. Instead, the interaction of Yrb1p with Xpo1p is mediated by Gsp1p-GTP. This novel type of export complex requires the acidic C-terminus of Gsp1p, which is dispensable for the binding to importin beta-like transport receptors. A similar complex with Xpo1p and Gsp1p-GTP can be formed by Yrb2p, a relative of Yrb1p predominantly located in the nucleus. Yrb1p also functions as a disassembly factor for NES/Xpo1p/Gsp1p-GTP complexes by displacing the NES protein from Xpo1p/Gsp1p. This Yrb1p/Xpo1p/Gsp1p complex is then completely dissociated after GTP hydrolysis catalyzed by the cytoplasmic GTPase activating protein Rna1p.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural insights into how Yrb2p accelerates the assembly of the Xpo1p nuclear export complex.Cell Rep. 2014 Nov 6;9(3):983-95. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.052. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25437554
-
Cex1p facilitates Rna1p-mediated dissociation of the Los1p-tRNA-Gsp1p-GTP export complex.Traffic. 2012 Feb;13(2):234-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01304.x. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Traffic. 2012. PMID: 22008473
-
Yrb4p, a yeast ran-GTP-binding protein involved in import of ribosomal protein L25 into the nucleus.EMBO J. 1997 Oct 15;16(20):6237-49. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.20.6237. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9321403 Free PMC article.
-
Review: transport of tRNA out of the nucleus-direct channeling to the ribosome?J Struct Biol. 2000 Apr;129(2-3):288-94. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.2000.4226. J Struct Biol. 2000. PMID: 10806079 Review.
-
Importin-beta-like nuclear transport receptors.Genome Biol. 2001;2(6):REVIEWS3008. doi: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-6-reviews3008. Epub 2001 Jun 5. Genome Biol. 2001. PMID: 11423015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atomic basis of CRM1-cargo recognition, release and inhibition.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Aug;27:52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24631835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RanBP2/RanGAP1*SUMO1/Ubc9 SUMO E3 ligase is a disassembly machine for Crm1-dependent nuclear export complexes.Nat Commun. 2016 May 10;7:11482. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11482. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27160050 Free PMC article.
-
A non-canonical mechanism for Crm1-export cargo complex assembly.Elife. 2015 Apr 21;4:e05745. doi: 10.7554/eLife.05745. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25895666 Free PMC article.
-
Pkh1 and Pkh2 differentially phosphorylate and activate Ypk1 and Ykr2 and define protein kinase modules required for maintenance of cell wall integrity.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Sep;13(9):3005-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-04-0201. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12221112 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Mpk1 cell wall integrity mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Swi6 transcriptional regulator.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 May 1;21(9):1609-19. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-11-0923. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20219973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitchison JD, Blobel G, Rout MP. Kap104p: a karyopherin involved in the nuclear transport of messenger RNA binding proteins. Science. 1996;274:624–627. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff FR, Görlich D. RanBP1 is crucial for the release of RanGTP from importin β-related nuclear transport factors. FEBS Lett. 1997;419:249–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

