Down-regulation of dendritic spine and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 expressions in the reelin haploinsufficient heterozygous reeler mouse
- PMID: 11248103
- PMCID: PMC30678
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051614698
Down-regulation of dendritic spine and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 expressions in the reelin haploinsufficient heterozygous reeler mouse
Abstract
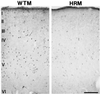
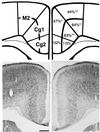
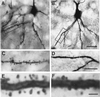
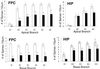
Heterozygous reeler mice (HRM) haploinsufficient for reelin express approximately 50% of the brain reelin content of wild-type mice, but are phenotypically different from both wild-type mice and homozygous reeler mice. They exhibit, (i) a down-regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD(67))-positive neurons in some but not every cortical layer of frontoparietal cortex (FPC), (ii) an increase of neuronal packing density and a decrease of cortical thickness because of neuropil hypoplasia, (iii) a decrease of dendritic spine expression density on basal and apical dendritic branches of motor FPC layer III pyramidal neurons, and (iv) a similar decrease in dendritic spines expressed on the basal dendrite branches of CA1 pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus. To establish whether the defect of GAD(67) down-regulation observed in HRM is responsible for neuropil hypoplasia and decreased dendritic spine density, we studied heterozygous GAD(67) knockout mice (HG(67)M). These mice exhibited a down-regulation of GAD(67) mRNA expression in FPC (about 50%), but they expressed normal amounts of reelin and had no neuropil hypoplasia or down-regulation of dendritic spine expression. These findings, coupled with electron-microscopic observations that reelin colocalizes with integrin receptors on dendritic spines, suggest that reelin may be a factor in the dynamic expression of cortical dendritic spines perhaps by promoting integrin receptor clustering. These findings are interesting because the brain neurochemical and neuroanatomical phenotypic traits exhibited by the HRM are in several ways similar to those found in postmortem brains of psychotic patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reelin in the extracellular matrix and dendritic spines of the cortex and hippocampus: a comparison between wild type and heterozygous reeler mice by immunoelectron microscopy.J Neurocytol. 2001 May;30(5):413-25. doi: 10.1023/a:1015017710332. J Neurocytol. 2001. PMID: 11951052
-
Region-specific alteration of GABAergic markers in the brain of heterozygous reeler mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Feb;33(4):689-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07563.x. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21226776
-
In Patas monkey, glutamic acid decarboxylase-67 and reelin mRNA coexpression varies in a manner dependent on layers and cortical areas.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Sep 23;451(3):279-88. doi: 10.1002/cne.10341. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12210139
-
GABAergic dysfunction in schizophrenia: new treatment strategies on the horizon.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Jul;180(2):191-205. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2212-8. Epub 2005 Apr 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15864560 Review.
-
Reelin down-regulation in mice and psychosis endophenotypes.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30(8):1065-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.04.001. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006. PMID: 16769115 Review.
Cited by
-
Saitohin polymorphism and executive dysfunction in schizophrenia.Neurol Sci. 2012 Oct;33(5):1051-6. doi: 10.1007/s10072-011-0893-9. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Neurol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22187337
-
Epigenetic mechanisms expressed in basal ganglia GABAergic neurons differentiate schizophrenia from bipolar disorder.Schizophr Res. 2007 Mar;91(1-3):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.11.029. Epub 2007 Jan 31. Schizophr Res. 2007. PMID: 17270400 Free PMC article.
-
A reelin-integrin receptor interaction regulates Arc mRNA translation in synaptoneurosomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 29;100(9):5479-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1031602100. Epub 2003 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12707415 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of somatostatin-positive dentate hilar interneurons induces age-related cellular changes and cognitive dysfunction.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Apr 13;2(5):pgad134. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad134. eCollection 2023 May. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 37168673 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal stress down-regulates Reelin expression by methylation of its promoter and induces adult behavioral impairments in rats.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0117680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117680. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25679528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weinberger D R, Berman K F, Zec R F. Arch Gen Psychol. 1986;43:114–124. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger D R, Lipska B K. Schizophr Res. 1995;16:87–110. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Kim J J, Potkin S G, Hetrick W P, Bunney W E, Jr, Jones E G. Arch Gen Psychol. 1996;53:425–436. - PubMed
-
- Selemon L D, Goldman-Rakic P S. Biol Psychol. 1999;45:17–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

