Eukaryotic ribonuclease P: increased complexity to cope with the nuclear pre-tRNA pathway
- PMID: 11241345
- PMCID: PMC3758117
- DOI: 10.1002/1097-4652(200104)187:1<11::AID-JCP1055>3.0.CO;2-K
Eukaryotic ribonuclease P: increased complexity to cope with the nuclear pre-tRNA pathway
Abstract
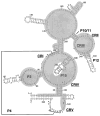
Ribonuclease P is an ancient enzyme that cleaves pre-tRNAs to generate mature 5' ends. It contains an essential RNA subunit in Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya, but the degree to which the RNA subunit relies on proteins to supplement catalysis is highly variable. The eukaryotic nuclear holoenzyme has recently been found to contain almost twenty times the protein content of the bacterial enzymes, in addition to having split into at least two related enzymes with distinct substrate specificity. In this review, recent progress in understanding the molecular architecture and functions of nuclear forms of RNase P will be considered.
Copyright 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence for an RNA-based catalytic mechanism in eukaryotic nuclear ribonuclease P.RNA. 2000 Apr;6(4):554-62. doi: 10.1017/s1355838200991477. RNA. 2000. PMID: 10786846 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 5' leader and 3' trailer structures on pre-tRNA processing by nuclear RNase P.Biochemistry. 2000 Aug 15;39(32):9909-16. doi: 10.1021/bi000603n. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10933810
-
Effects of phosphorothioate modifications on precursor tRNA processing by eukaryotic RNase P enzymes.J Mol Biol. 2000 May 12;298(4):559-65. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3655. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10788319
-
Eukaryotic ribonuclease P: a plurality of ribonucleoprotein enzymes.Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:165-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135352. Epub 2001 Nov 9. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12045094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribonuclease P from plant nuclei and photosynthetic organelles.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):139-45. doi: 10.1007/BF00988719. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901501 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential roles of Bdp1, a subunit of RNA polymerase III initiation factor TFIIIB, in transcription and tRNA processing.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(10):3264-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3264-3275.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11971960 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of Rpp25, an RNA-binding protein subunit of human ribonuclease P.RNA. 2002 Mar;8(3):290-5. doi: 10.1017/s1355838202027954. RNA. 2002. PMID: 12003489 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of TRZ1, a yeast homolog of the human candidate prostate cancer susceptibility gene ELAC2 encoding tRNase Z.BMC Mol Biol. 2005 May 13;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-6-12. BMC Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15892892 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae pre-tRNA processing by environmental conditions.RNA. 2016 Mar;22(3):339-49. doi: 10.1261/rna.054973.115. Epub 2016 Jan 4. RNA. 2016. PMID: 26729922 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic analysis of the structure of RNase MRP RNA in yeasts.RNA. 2002 Jun;8(6):740-51. doi: 10.1017/s1355838202022082. RNA. 2002. PMID: 12088147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaboshi E, Guerrier-Takada C, Altman S. Veal heart ribonuclease P has an essential RNA component. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980;96:831–837. - PubMed
-
- Alifano P, Rivellini F, Piscitelli C, Arraiano CM, Bruni CB, Carlomagno MS. Ribonuclease E provides substrates for ribonuclease P-dependent processing of a polycistronic mRNA. Genes Dev. 1994;8:3021–3031. - PubMed
-
- Altman S, Wesolowski D, Puranam RS. Nucleotide sequences of the RNA subunit of RNase P from several mammals. Genomics. 1993;18:418–422. - PubMed
-
- Arends S, Schon A. Partial purification and characterization of nuclear ribonuclease P from wheat. Eur J Biochem. 1997;244:635–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

