The relationship between spontaneous telomere loss and chromosome instability in a human tumor cell line
- PMID: 11228547
- PMCID: PMC1508089
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900107
The relationship between spontaneous telomere loss and chromosome instability in a human tumor cell line
Abstract
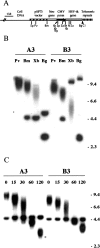
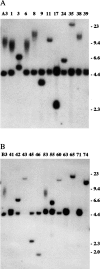
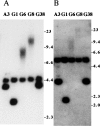
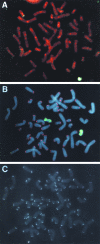
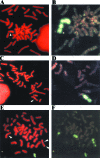
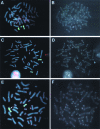
Chromosome instability plays an important role in cancer by promoting the alterations in the genome required for tumor cell progression. The loss of telomeres that protect the ends of chromosomes and prevent chromosome fusion has been proposed as one mechanism for chromosome instability in cancer cells, however, there is little direct evidence to support this hypothesis. To investigate the relationship between spontaneous telomere loss and chromosome instability in human cancer cells, clones of the EJ-30 tumor cell line were isolated in which a herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV-tk) gene was integrated immediately adjacent to a telomere. Selection for HSV-tk-deficient cells with ganciclovir demonstrated a high rate of loss of the end these "marked" chromosomes (10-4 events/cell per generation). DNA sequence and cytogenetic analysis suggests that the loss of function of the HSV-tk gene most often involves telomere loss, sister chromatid fusion, and prolonged periods of chromosome instability. In some HSV-tk-deficient cells, telomeric repeat sequences were added on to the end of the truncated HSV-tk gene at a new location, whereas in others, no telomere was detected on the end of the marked chromosome. These results suggest that spontaneous telomere loss is a mechanism for chromosome instability in human cancer cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DNA amplification by breakage/fusion/bridge cycles initiated by spontaneous telomere loss in a human cancer cell line.Neoplasia. 2002 Nov-Dec;4(6):531-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900267. Neoplasia. 2002. PMID: 12407447 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of interstitial telomeric sequences on chromosome instability in human cells.Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1999;86(3-4):288-95. doi: 10.1159/000015321. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1999. PMID: 10575228
-
Chromosome instability as a result of double-strand breaks near telomeres in mouse embryonic stem cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4836-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4836-4850.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052890 Free PMC article.
-
Telomeres and chromosome instability.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Sep 8;5(9-10):1082-92. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.030. Epub 2006 Jun 19. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16784900 Review.
-
Telomere dysfunction and chromosome instability.Mutat Res. 2012 Feb 1;730(1-2):28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.04.008. Epub 2011 May 7. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 21575645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput screen to identify compounds that prevent or target telomere loss in human cancer cells.NAR Cancer. 2022 Oct 3;4(4):zcac029. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcac029. eCollection 2022 Dec. NAR Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36196242 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Hot Spots of De Novo Telomere Addition in the Yeast Genome Contain Proximal Enhancers That Bind Cdc13.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 May 31;36(12):1750-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00095-16. Print 2016 Jun 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27044869 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of telomere loss and their consequences for chromosome instability.Front Oncol. 2012 Oct 4;2:135. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00135. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23061048 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere Length Dynamics and the Evolution of Cancer Genome Architecture.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 6;19(2):482. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020482. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29415479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subtelomeric regions in mammalian cells are deficient in DNA double-strand break repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 May 5;10(5):536-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Apr 3. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21466975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blackburn EH, Greider CW, editors. Telomeres. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1995.
-
- de Lange T. Telomere dynamics and genome instability in human cancer. In: Blackburn EH , Greider CW, editors. Telomeres. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 1995. pp. 265–293.
-
- Hastie ND, Allshire RC. Human telomeres: fusion and interstitial sites. Trends Genet. 1989;5:326–331. - PubMed
-
- Conrad MN, Dominguez AM, Dresser ME. Ndj1p, a meiotic telomere protein required for normal chromosome synapsis and segregation in yeast. Science. 1997;276:1252–1255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
