A novel silencer element in the bovine papillomavirus type 4 promoter represses the transcriptional response to papillomavirus E2 protein
- PMID: 11222708
- PMCID: PMC115909
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.6.2829-2838.2001
A novel silencer element in the bovine papillomavirus type 4 promoter represses the transcriptional response to papillomavirus E2 protein
Abstract
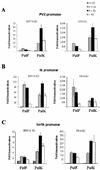
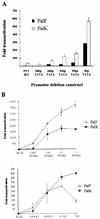
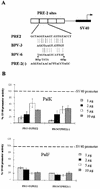
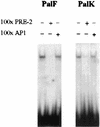
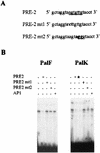
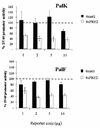
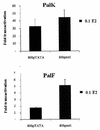
The long control regions (LCRs) of mucosal epitheliotropic papillomaviruses have similar organizations: a promoter region, an enhancer region, and a highly conserved distribution of E2 DNA binding sites (C. Desaintes and C. Demeret, Semin. Cancer Biol. 7:339--347, 1996). The enhancer of these viruses is epithelial cell specific, as it fails to activate transcription from heterologous promoters in nonepithelial cell types (B. Gloss, H. U. Bernard, K. Seedorf, and G. Klock, EMBO J. 6:3735--3743, 1987). Using the bovine papillomavirus type 4 (BPV-4) LCR and a bovine primary cell system, we have shown previously that a level of epithelial specificity resides in a papillomavirus promoter region. The BPV-4 promoter shows an enhanced response to transcriptional activators in epithelial cells compared with that of fibroblasts (K. W. Vance, M. S. Campo, and I. M. Morgan, J. Biol. Chem. 274:27839--27844, 1999). A chimeric lcr/tk promoter suggests that the upstream BPV-4 promoter region determines the cell-type-selective response of this promoter in fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Promoter deletion analysis identified two novel repressor elements that are, at least in part, responsible for mediating the differential response of this promoter to upstream activators in fibroblasts and keratinocytes. One of these elements, promoter repressor element 2 (PRE-2), is conserved in position and sequence in the related mucosal epitheliotropic papillomaviruses, BPV-3 and BPV-6. PRE-2 functions in cis to repress the basal activity of the simian virus 40 promoter and binds a specific protein complex. We identify the exact nucleotides necessary for binding and correlate loss of binding with loss of transcriptional repression. We also incorporate these mutations into the BPV-4 promoter and demonstrate an enhanced response of the mutated promoter to E2 in fibroblasts. The DNA binding protein in the detected complex is shown to have a molecular mass of approximately 50 kDa. The PRE-2 binding protein represents a novel transcriptional repressor and regulator of papillomavirus transcription.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epithelial specific transcriptional regulation of the bovine papillomavirus 4 promoter by E2.J Gen Virol. 1998 Mar;79 ( Pt 3):501-8. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-79-3-501. J Gen Virol. 1998. PMID: 9519828
-
An enhanced epithelial response of a papillomavirus promoter to transcriptional activators.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 24;274(39):27839-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.39.27839. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10488130
-
Adeno-associated virus Rep78 binds to E2-responsive element 1 of bovine papillomavirus type 1.IUBMB Life. 1999 Oct;48(4):397-404. doi: 10.1080/713803543. IUBMB Life. 1999. PMID: 10632568
-
Papillomavirus transforming functions.Ciba Found Symp. 1986;120:39-52. doi: 10.1002/9780470513309.ch4. Ciba Found Symp. 1986. PMID: 3013525 Review.
-
The papillomavirus E2 protein: a factor with many talents.Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):440-4. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90172-r. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991. PMID: 1663669 Review.
Cited by
-
TopBP1 regulates human papillomavirus type 16 E2 interaction with chromatin.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(8):4338-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02353-06. Epub 2007 Feb 7. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17287259 Free PMC article.
-
An interaction between human papillomavirus 16 E2 and TopBP1 is required for optimum viral DNA replication and episomal genome establishment.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):12806-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01002-12. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22973044 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 Phosphorylation of Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 on Serine 23 Promotes Interaction with TopBP1 and Is Critical for E2 Interaction with Mitotic Chromatin and the Viral Life Cycle.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0116321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01163-21. Epub 2021 Sep 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34544280 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of miRNA expression under stress in Arabidopsis thaliana.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2012 Aug;12(3):169-76. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2012.2471. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22938544 Free PMC article.
-
Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) E2 Repression of TWIST1 Transcription Is a Potential Mediator of HPV16 Cancer Outcomes.mSphere. 2020 Dec 9;5(6):e00981-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00981-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 33298572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apt D, Watts R M, Suske G, Bernard H U. High Sp1-Sp3 ratios in epithelial cells during epithelial differentiation and cellular transformation correlate with the activation of the HPV-16 promoter. Virology. 1996;224:281–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

