Lowering S-adenosylmethionine levels in Escherichia coli modulates C-to-T transition mutations
- PMID: 11208790
- PMCID: PMC94959
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.3.921-927.2001
Lowering S-adenosylmethionine levels in Escherichia coli modulates C-to-T transition mutations
Abstract
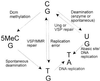
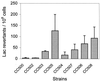
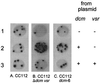
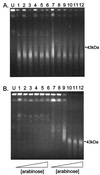
Deoxycytosine methylase (Dcm) enzyme activity causes mutagenesis in vitro either directly by enzyme-induced deamination of cytosine to uracil in the absence of the methyl donor, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), or indirectly through spontaneous deamination of [5-methyl]cytosine to thymine. Using a Lac reversion assay, we investigated the contribution of the first mechanism to Dcm mutagenesis in vivo by lowering the levels of SAM. Escherichia coli SAM levels were lowered by reducing SAM synthetase activity via the introduction of a metK84 allele or by hydrolyzing SAM using the bacteriophage T3 SAM hydrolase. The metK84 strains exhibited increased C-to-T mutagenesis. Expression of the T3 SAM hydrolase gene, under the control of the arabinose-inducible P(BAD) promoter, effectively reduced Dcm-mediated genomic DNA methylation. However, increased mutagenesis was not observed until extremely high arabinose concentrations were used, and genome methylation at Dcm sites was negligible.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms for the involvement of DNA methylation in colon carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 1996 May 15;56(10):2375-81. Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8625314
-
A cytosine methyltransferase converts 5-methylcytosine in DNA to thymine.Biochemistry. 1995 Nov 14;34(45):14752-7. doi: 10.1021/bi00045a016. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 7578083
-
HhaI and HpaII DNA methyltransferases bind DNA mismatches, methylate uracil and block DNA repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Apr 25;23(8):1380-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.8.1380. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995. PMID: 7753629 Free PMC article.
-
The repair of 5-methylcytosine deamination damage.EXS. 1993;64:510-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9118-9_23. EXS. 1993. PMID: 8380355 Review. No abstract available.
-
Principal causes of hot spots for cytosine to thymine mutations at sites of cytosine methylation in growing cells. A model, its experimental support and implications.Mutat Res. 1999 Jul;437(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(99)00065-4. Mutat Res. 1999. PMID: 10425387 Review.
Cited by
-
A cytosine methyltransferase homologue is essential for repeat-induced point mutation in Neurospora crassa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 25;99(13):8802-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.132212899. Epub 2002 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12072568 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse functions of restriction-modification systems in addition to cellular defense.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013 Mar;77(1):53-72. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00044-12. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23471617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health considerations regarding horizontal transfer of microbial transgenes present in genetically modified crops.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2005;2005(4):326-52. doi: 10.1155/JBB.2005.326. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16489267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharya S K, Dubey A K. Kinetic mechanism of cytosine DNA methyltransferase MspI. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:14743–14749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

