The role of TNF-receptor family members and other TRAF-dependent receptors in bone resorption
- PMID: 11178122
- PMCID: PMC128878
- DOI: 10.1186/ar134
The role of TNF-receptor family members and other TRAF-dependent receptors in bone resorption
Abstract
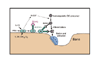
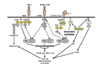
The contribution of osteoclasts to the process of bone loss in inflammatory arthritis has recently been demonstrated. Studies in osteoclast biology have led to the identification of factors responsible for the differentiation and activation of osteoclasts, the most important of which is the receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand/osteoclast differentiation factor (RANKL/ODF), a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like protein. The RANKL/ODF receptor, receptor activator of NF-kappa B (RANK), is a TNF-receptor family member present on both osteoclast precursors and mature osteoclasts. Like other TNF-family receptors and the IL-1 receptor, RANK mediates its signal transduction via TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) proteins, suggesting that the signaling pathways activated by RANK and other inflammatory cytokines involved in osteoclast differentiation and activation are interconnected.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of RANKL in physiological and pathological bone resorption and therapeutics targeting the RANKL-RANK signaling system.Immunol Rev. 2005 Dec;208:30-49. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00327.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16313339 Review.
-
A new member of tumor necrosis factor ligand family, ODF/OPGL/TRANCE/RANKL, regulates osteoclast differentiation and function.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Mar 24;256(3):449-55. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0252. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10080918 Review.
-
Cross-talk between the interleukin-6 and prostaglandin E(2) signaling systems results in enhancement of osteoclastogenesis through effects on the osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor-{kappa}B (RANK) ligand/RANK system.Endocrinology. 2005 Apr;146(4):1991-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1167. Epub 2004 Dec 23. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15618359
-
T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma.Nature. 2000 Nov 30;408(6812):600-5. doi: 10.1038/35046102. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11117749
-
Osteoclast precursors, RANKL/RANK, and immunology.Immunol Rev. 2005 Dec;208:19-29. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00336.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16313338 Review.
Cited by
-
[Bone metabolism: molecular mechanisms].Z Rheumatol. 2007 Jul;66(4):286-9. doi: 10.1007/s00393-007-0182-4. Z Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17562055 Review. German.
-
Joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: interactions between tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) regulate osteoclasts.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Apr;63(4):354-9. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.008458. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15020327 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic variant in osteoprotegerin is associated with progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 May 7;16(3):R108. doi: 10.1186/ar4558. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24886600 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental arthritis in CC chemokine receptor 2-null mice closely mimics severe human rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Invest. 2004 Mar;113(6):856-66. doi: 10.1172/JCI20126. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15067318 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from animal models of arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002 Jun;4(3):232-9. doi: 10.1007/s11926-002-0070-5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002. PMID: 12010608 Review.
References
-
- Leisen JCC, Duncan H, Riddle JM, Pitchford WC. The erosive front: a topographic study of the junction between the pannus and the subchondral plate in the macerated rheumatoid metacarpal head. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Bromley M, Woolley DE. Chondroclasts and osteoclasts at subchondral sites of erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27:968–975. - PubMed
-
- Romas E, Bakharevski O, Hards DK, Kartsogiannis V, Quinn JMW, Ryan PFJ, Martin J, Gillespie MT. Expression of osteoclast differentiation factor at sites of bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:821–826. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y, Nishikaku F, Nakatuka M, Koga Y. Osteoclast-like cells in murine collagen induced arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:1154–1160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

