Structure and function of a vimentin-associated matrix adhesion in endothelial cells
- PMID: 11160825
- PMCID: PMC30570
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.1.85
Structure and function of a vimentin-associated matrix adhesion in endothelial cells
Abstract
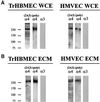
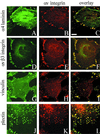
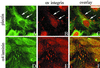
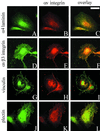
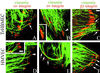
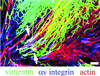
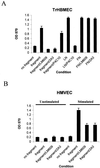
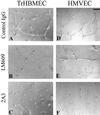
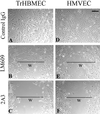
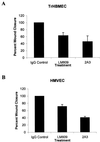
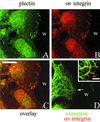
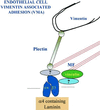
The alpha4 laminin subunit is a component of endothelial cell basement membranes. An antibody (2A3) against the alpha4 laminin G domain stains focal contact-like structures in transformed and primary microvascular endothelial cells (TrHBMECs and HMVECs, respectively), provided the latter cells are activated with growth factors. The 2A3 antibody staining colocalizes with that generated by alphav and beta3 integrin antibodies and, consistent with this localization, TrHBMECs and HMVECs adhere to the alpha4 laminin subunit G domain in an alphavbeta3-integrin-dependent manner. The alphavbeta3 integrin/2A3 antibody positively stained focal contacts are recognized by vinculin antibodies as well as by antibodies against plectin. Unusually, vimentin intermediate filaments, in addition to microfilament bundles, interact with many of the alphavbeta3 integrin-positive focal contacts. We have investigated the function of alpha4-laminin and alphavbeta3-integrin, which are at the core of these focal contacts, in cultured endothelial cells. Antibodies against these proteins inhibit branching morphogenesis of TrHBMECs and HMVECs in vitro, as well as their ability to repopulate in vitro wounds. Thus, we have characterized an endothelial cell matrix adhesion, which shows complex cytoskeletal interactions and whose assembly is regulated by growth factors. Our data indicate that this adhesion structure may play a role in angiogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of the association of alpha 6 beta 4 with vimentin intermediate filaments in endothelial cells.Exp Cell Res. 2002 Nov 15;281(1):107-14. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5643. Exp Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 12441134
-
Complex interactions between the laminin alpha 4 subunit and integrins regulate endothelial cell behavior in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 10;99(25):16075-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.252649399. Epub 2002 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12454288 Free PMC article.
-
The alpha4 laminin subunit regulates endothelial cell survival.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Mar 10;294(1):281-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2003.11.006. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 14980521
-
The role of laminin in attachment, growth, and differentiation of cultured cells: a brief review.Cytotechnology. 1992;9(1-3):99-106. doi: 10.1007/BF02521736. Cytotechnology. 1992. PMID: 1369186 Review.
-
Laminin binding conveys mechanosensing in endothelial cells.News Physiol Sci. 2002 Aug;17:166-9. doi: 10.1152/nips.01381.2001. News Physiol Sci. 2002. PMID: 12136046 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of endogenous FAK via expression of its amino terminal domain in Xenopus embryos.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042577. Epub 2012 Aug 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22880041 Free PMC article.
-
Laminin deposition in the extracellular matrix: a complex picture emerges.J Cell Sci. 2009 Dec 15;122(Pt 24):4409-17. doi: 10.1242/jcs.041095. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19955338 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Mechanosensation and Mechanotransduction in Vascular Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 17;10:905927. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.905927. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35784481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA hypermethylation of the vimentin gene inversely correlates with vimentin expression in intestinal- and diffuse-type gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2016 Jan;11(1):842-848. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3937. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26870294 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of vimentin impairs endothelial differentiation of embryonic stem cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 2;6:30814. doi: 10.1038/srep30814. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27480130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker SE, Hopkinson SB, Fitchmun M, Andreason GL, Frasier F, Plopper G, Quaranta V, Jones JCR. Laminin-5 and hemidesmosomes: role of the alpha 3 chain subunit in hemidesmosome stability and assembly. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:2509–2520. - PubMed
-
- Bershadsky AD, Tint IS, Svitkina TM. Association of intermediate filaments with vinculin-containing adhesion plaques of fibroblasts. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;8:274–283. - PubMed
-
- Brooks PC, Clark RAF, Cheresh DA. Requirement of vascular integrin αvβ3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994a;264:569–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

