A novel neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) binding protein, WISH, induces Arp2/3 complex activation independent of Cdc42
- PMID: 11157975
- PMCID: PMC2196001
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.3.471
A novel neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) binding protein, WISH, induces Arp2/3 complex activation independent of Cdc42
Abstract
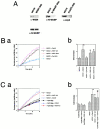
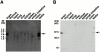
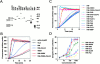
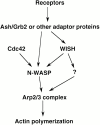
We identified a novel adaptor protein that contains a Src homology (SH)3 domain, SH3 binding proline-rich sequences, and a leucine zipper-like motif and termed this protein WASP interacting SH3 protein (WISH). WISH is expressed predominantly in neural tissues and testis. It bound Ash/Grb2 through its proline-rich regions and neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) through its SH3 domain. WISH strongly enhanced N-WASP-induced Arp2/3 complex activation independent of Cdc42 in vitro, resulting in rapid actin polymerization. Furthermore, coexpression of WISH and N-WASP induced marked formation of microspikes in Cos7 cells, even in the absence of stimuli. An N-WASP mutant (H208D) that cannot bind Cdc42 still induced microspike formation when coexpressed with WISH. We also examined the contribution of WISH to a rapid actin polymerization induced by brain extract in vitro. Arp2/3 complex was essential for brain extract-induced rapid actin polymerization. Addition of WISH to extracts increased actin polymerization as Cdc42 did. However, WISH unexpectedly could activate actin polymerization even in N-WASP-depleted extracts. These findings suggest that WISH activates Arp2/3 complex through N-WASP-dependent and -independent pathways without Cdc42, resulting in the rapid actin polymerization required for microspike formation.
Figures


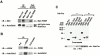



Similar articles
-
GRB2 links signaling to actin assembly by enhancing interaction of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASp) with actin-related protein (ARP2/3) complex.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):21946-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000687200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10781580
-
A complex of N-WASP and WIP integrates signalling cascades that lead to actin polymerization.Nat Cell Biol. 2000 Jul;2(7):441-8. doi: 10.1038/35017080. Nat Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10878810
-
Identification of another actin-related protein (Arp) 2/3 complex binding site in neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) that complements actin polymerization induced by the Arp2/3 complex activating (VCA) domain of N-WASP.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 31;276(35):33175-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102866200. Epub 2001 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11432863
-
[Reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton by WASP family proteins].Seikagaku. 2002 Sep;74(9):1149-61. Seikagaku. 2002. PMID: 12402455 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Signalling to actin: the Cdc42-N-WASP-Arp2/3 connection.Chem Biol. 1999 Sep;6(9):R235-40. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(99)80107-0. Chem Biol. 1999. PMID: 10467124 Review.
Cited by
-
Acroplaxome, an F-actin-keratin-containing plate, anchors the acrosome to the nucleus during shaping of the spermatid head.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Nov;14(11):4628-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-04-0226. Epub 2003 Aug 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14551252 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of dip1p reveals a switch in Arp2/3-dependent actin assembly for fission yeast endocytosis.Curr Biol. 2011 Jun 7;21(11):905-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.04.047. Epub 2011 May 27. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21620704 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular impact of Psoriasin (S100A7) on the healing of human wounds.Exp Ther Med. 2017 May;13(5):2151-2160. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4275. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28565822 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the nucleation-promoting factor SPIN90 bound to the actin filament nucleator Arp2/3 complex.EMBO J. 2018 Nov 15;37(22):e100005. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018100005. Epub 2018 Oct 15. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 30322896 Free PMC article.
-
Actin nucleation and elongation factors: mechanisms and interplay.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;21(1):28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.12.001. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19168341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L.M., Cherniack A.D., Klarlund J.K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M.P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993;260:1950–1952. - PubMed
-
- Carlier M.F., Nioche P., Broutin-L'Hermite I., Boujemaa R., Le Clainche R.C., Egile C., Garbay C., Ducruix A., Sansonetti P., Pantaloni D. GRB2 links signaling to actin assembly by enhancing interaction of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASp) with actin-related protein (ARP2/3) complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:21946–21952. - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M.H., Miki H., Takenawa T. Identification of N-WASP homologs in human and rat brain. Gene. 1997;196:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Feller S.M., Ren R., Hanafusa H., Baltimore D. SH2 and SH3 domains as molecular adhesivesthe interactions of Crk and Abl. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994;19:453–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

