Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA2 is a B-cell-specific latent viral protein that inhibits p53
- PMID: 11119611
- PMCID: PMC113935
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.1.429-438.2001
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA2 is a B-cell-specific latent viral protein that inhibits p53
Abstract
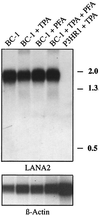
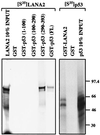
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), or human herpesvirus 8, is associated with three proliferative diseases ranging from viral cytokine-induced hyperplasia to monoclonal neoplasia: multicentric Castleman's disease (CD), Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). Here we report a new latency-associated 1,704-bp KSHV spliced gene belonging to a cluster of KSHV sequences having homology to the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) family of transcription factors. ORFK10.5 encodes a protein, latency-associated nuclear antigen 2 (LANA2), which is expressed in KSHV-infected hematopoietic tissues, including PEL and CD but not KS lesions. LANA2 is abundantly expressed in the nuclei of cultured KSHV-infected B cells. Transcription of K10.5 in PEL cell cultures is not inhibited by DNA polymerase inhibitors nor significantly induced by phorbol ester treatment. Unlike LANA1, LANA2 does not elicit a serologic response from patients with KS, PEL, or CD as measured by Western blot hybridization. Both KSHV vIRF1 (ORFK9) and LANA2 (ORFK10.5) appear to have arisen through gene duplication of a captured cellular IRF gene. LANA2 is a potent inhibitor of p53-induced transcription in reporter assays. LANA2 antagonizes apoptosis due to p53 overexpression in p53-null SAOS-2 cells and apoptosis due to doxorubicin treatment of wild-type p53 U2OS cells. While LANA2 specifically interacts with amino acids 290 to 393 of p53 in glutathione S-transferase pull-down assays, we were unable to demonstrate LANA2-p53 interaction in vivo by immunoprecipitation. These findings show that KSHV has tissue-specific latent gene expression programs and identify a new latent protein which may contribute to KSHV tumorigenesis in hematopoietic tissues via p53 inhibition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
p53 inhibition by the LANA protein of KSHV protects against cell death.Nature. 1999 Dec 23-30;402(6764):889-94. doi: 10.1038/47266. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10622254
-
Recruitment of the tumour suppressor protein p73 by Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus latent nuclear antigen contributes to the survival of primary effusion lymphoma cells.Oncogene. 2013 Aug 8;32(32):3676-85. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.385. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22964633
-
Latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interacts with human myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen induced by interferon alpha.Virus Genes. 2003 Dec;27(3):237-47. doi: 10.1023/a:1026391715071. Virus Genes. 2003. PMID: 14618084
-
The KSHV latency-associated nuclear antigen: a multifunctional protein.Front Biosci. 2002 Mar 1;7:d726-30. doi: 10.2741/komatsu. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11861213 Review.
-
The Kaposi' s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen.Viral Immunol. 2001;14(4):311-7. doi: 10.1089/08828240152716565. Viral Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11792061 Review.
Cited by
-
KSHV-Mediated Angiogenesis in Tumor Progression.Viruses. 2016 Jul 20;8(7):198. doi: 10.3390/v8070198. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27447661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global changes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated virus gene expression patterns following expression of a tetracycline-inducible Rta transactivator.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):4205-20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.4205-4220.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12634378 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the bipartite nuclear localization signal of protein LANA2 from Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Biochem J. 2003 Sep 1;374(Pt 2):545-50. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021890. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12767255 Free PMC article.
-
Surface downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I, PE-CAM, and ICAM-1 following de novo infection of endothelial cells with Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9669-84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9669-9684.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915579 Free PMC article.
-
p53 tumor suppressor protein stability and transcriptional activity are targeted by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded viral interferon regulatory factor 3.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;34(3):386-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01011-13. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24248600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bais C, Santomasso B, Coso O, Arvanitakis L, Geras Raaka E, Gutkind J S, Asch A S, Cesarman E, Gerhengorn M C, Mesri E A. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature. 1998;391:86–89. - PubMed
-
- Ballestas M E, Chatis P A, Kaye K M. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science. 1999;284:641–644. - PubMed
-
- Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown J P, Sedivy J M, Kinzler K W, Vogelstein B. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science. 1998;282:1497–1501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

