Epstein-Barr virus-encoded poly(A)(-) RNA supports Burkitt's lymphoma growth through interleukin-10 induction
- PMID: 11118209
- PMCID: PMC305895
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6742
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded poly(A)(-) RNA supports Burkitt's lymphoma growth through interleukin-10 induction
Abstract
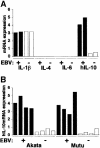
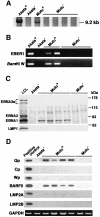
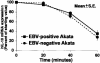
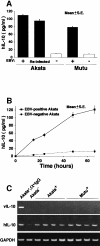
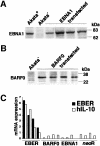
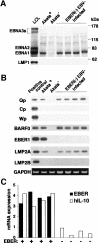
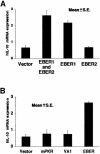
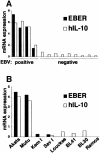
Akata and Mutu cell lines are derived from Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) and retain the in vivo phenotype of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) expression that is characterized by expression of EBV-determined nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1), EBV-encoded RNAs (EBERs) and transcripts from the BAM:HI A region (BARF0). We found that EBV-positive Akata and Mutu cell clones expressed higher levels of interleukin (IL)-10 than their EBV-negative subclones at the transcriptional level. Transfection of an individual EBV latent gene into EBV-negative Akata cells revealed that EBERs were responsible for IL-10 induction. Recombinant IL-10 enabled EBV-negative Akata cells to grow in low (0.1%) serum conditions. On the other hand, growth of EBV-positive Akata cells was blocked by treatment either with an anti-IL-10 antibody or antisense oligonucleotide against IL-10. EBV-positive BL biopsies consistently expressed IL-10, but EBV-negative BL biopsies did not. These results suggest that IL-10 induced by EBERs acts as an autocrine growth factor for BL. EBERs, EBER1 and EBER2, are non-polyadenylated RNAs and are 166 and 172 nucleotides long, respectively. The present findings indicate that RNA molecules could regulate cell growth.
Figures

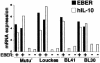
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus encoded BALF1 gene is transcribed in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines and in nasopharyngeal carcinoma's biopsies.J Clin Virol. 2005 Sep;34(1):26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.12.016. J Clin Virol. 2005. PMID: 16087121
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded RNA promotes growth of EBV-infected T cells through interleukin-9 induction.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;64(15):5332-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0733. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15289339
-
Replacement of the Epstein-Barr virus plasmid with the EBER plasmid in Burkitt's lymphoma cells.J Virol. 2001 Oct;75(20):9977-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.20.9977-9982.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11559830 Free PMC article.
-
The role of EBERs in oncogenesis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):461-7. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2001.0413. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001. PMID: 11669608 Review.
-
The role of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) in oncogenesis.Rev Med Virol. 2002 Sep-Oct;12(5):321-6. doi: 10.1002/rmv.363. Rev Med Virol. 2002. PMID: 12211044 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral noncoding RNAs: more surprises.Genes Dev. 2015 Mar 15;29(6):567-84. doi: 10.1101/gad.259077.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25792595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1beta expression in human gastric carcinoma with Epstein-Barr virus infection.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(13):6825-31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.13.6825-6831.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12050395 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded RNA 2 (EBER2) but not EBER1 plays a critical role in EBV-induced B-cell growth transformation.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(20):11236-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00579-07. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17686859 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine signaling pathway polymorphisms and AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk in the multicenter AIDS cohort study.AIDS. 2010 Apr 24;24(7):1025-33. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328332d5b1. AIDS. 2010. PMID: 20299965 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo signaling effectors YAP and TAZ induce Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) lytic reactivation through TEADs in epithelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Aug 2;17(8):e1009783. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009783. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34339458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baer R. et al. (1984) DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein–Barr virus genome. Nature, 310, 207–211. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin D., Knobloch,T.J. and Dayton,M.A. (1992) Human B-cell interleukin-10: B-cell lines derived from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and Burkitt’s lymphoma constitutively secrete a large quantity of interleukin-10. Blood, 80, 1289–1298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

