Structural organization of yeast and mammalian mediator complexes
- PMID: 11114191
- PMCID: PMC18914
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.260489497
Structural organization of yeast and mammalian mediator complexes
Abstract
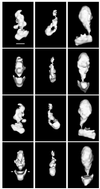
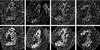
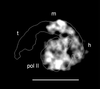
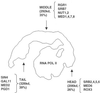
Structures of yeast Mediator complex, of a related complex from mouse cells and of thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex from human cells have been determined by three-dimensional reconstruction from electron micrographs of single particles. All three complexes show a division in two parts, a "head" domain and a combined "middle-tail" domain. The head domains of the three complexes appear most similar and interact most closely with RNA polymerase II. The middle-tail domains show the greatest structural divergence and, in the case of the tail domain, may not interact with polymerase at all. Consistent with this structural divergence, analysis of a yeast Mediator mutant localizes subunits that are not conserved between yeast and mammalian cells to the tail domain. Biochemically defined Rgr1 and Srb4 modules of yeast Mediator are then assigned to the middle and head domains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The classical srb4-138 mutant allele causes dissociation of yeast Mediator.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Oct 27;349(3):948-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.08.099. Epub 2006 Aug 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16962561
-
The structural and functional organization of the yeast mediator complex.J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 9;276(45):42003-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105961200. Epub 2001 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11555651
-
Head module control of mediator interactions.Mol Cell. 2006 Aug 4;23(3):355-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.007. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16885025
-
Twenty years of Mediator complex structural studies.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Feb 28;47(1):399-410. doi: 10.1042/BST20180608. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30733343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of co-activators and co-repressors in the mechanism of steroid/thyroid receptor action.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:141-64; discussion 164-5. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997. PMID: 9238851 Review.
Cited by
-
The functions of Mediator in Candida albicans support a role in shaping species-specific gene expression.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(4):e1002613. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002613. Epub 2012 Apr 5. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22496666 Free PMC article.
-
Tail and Kinase Modules Differently Regulate Core Mediator Recruitment and Function In Vivo.Mol Cell. 2016 Nov 3;64(3):455-466. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27773677 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular architecture of the yeast Mediator complex.Elife. 2015 Sep 24;4:e08719. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08719. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26402457 Free PMC article.
-
Functional metabolomics as a tool to analyze Mediator function and structure in plants.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 22;12(6):e0179640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179640. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28640868 Free PMC article.
-
Toward understanding of the mechanisms of Mediator function in vivo: Focus on the preinitiation complex assembly.Transcription. 2017;8(5):328-342. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1329000. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Transcription. 2017. PMID: 28841352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flanagan P M, Kelleher R J, Sayre M H, III, Tschochner H, Kornberg R D. Nature (London) 1991;350:436–438. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y J, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre M H, Kornberg R D. Cell. 1994;77:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Ito M, Yuan C X, Malik S, Gu W, Fondell J D, Yamamura S, Fu Z Y, Zhang X, Qin J, Roeder R G. Mol Cell. 1999;3:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Naar A M, Beaurang P A, Zhou S, Abraham S, Solomon W, Tjian R. Nature (London) 1999;398:828–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

