Abolition of male sexual behaviors in mice lacking estrogen receptors alpha and beta (alpha beta ERKO)
- PMID: 11114183
- PMCID: PMC18988
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.250473597
Abolition of male sexual behaviors in mice lacking estrogen receptors alpha and beta (alpha beta ERKO)
Abstract
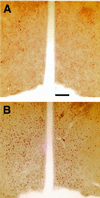
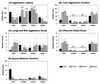
Male mice with a knockout of the estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha gene, a ligand-activated transcription factor, showed reduced levels of intromissions and no ejaculations whereas simple mounting behavior was not affected. In contrast, all components of sexual behaviors were intact in male mice lacking the novel ER-beta gene. Here we measure the extent of phenotype in mice that lack both ER-alpha and ER-beta genes (alphabetaERKO). alphabetaERKO male mice did not show any components of sexual behaviors, including simple mounting behavior. Nor did they show ultrasonic vocalizations during behavioral tests with receptive female mice. On the other hand, reduced aggressive behaviors of alphabetaERKO mice mimicked those of single knockout mice of ER-alpha gene (alphaERKO). They showed reduced levels of lunge and bite aggression, but rarely showed offensive attacks. Thus, either one of the ERs is sufficient for the expression of simple mounting in male mice, indicating a redundancy in function. Offensive attacks, on the other hand, depend specifically on the ER-alpha gene. Different patterns of natural behaviors require different patterns of functions by ER genes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Another role highlighted for estrogens in the male: sexual behavior.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14038-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011526097. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11114169 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Modifications of testosterone-dependent behaviors by estrogen receptor-alpha gene disruption in male mice.Endocrinology. 1998 Dec;139(12):5058-69. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.12.6358. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9832445
-
Roles of estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression in reproduction-related behaviors in female mice.Endocrinology. 1998 Dec;139(12):5070-81. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.12.6357. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9832446
-
Genotype/age interactions on aggressive behavior in gonadally intact estrogen receptor beta knockout (betaERKO) male mice.Horm Behav. 2002 May;41(3):288-96. doi: 10.1006/hbeh.2002.1773. Horm Behav. 2002. PMID: 11971662
-
Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us?Endocr Rev. 1999 Jun;20(3):358-417. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.3.0370. Endocr Rev. 1999. PMID: 10368776 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor knockout mice: phenotypes in the female reproductive tract.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2003 Apr;17(2):169-76. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12737678 Review.
Cited by
-
Behavioral analysis of genetically modified mice indicates essential roles of neurosteroidal estrogen.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2011 Sep 26;2:40. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2011.00040. eCollection 2011. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2011. PMID: 22654807 Free PMC article.
-
The androgen receptor governs the execution, but not programming, of male sexual and territorial behaviors.Neuron. 2010 Apr 29;66(2):260-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.024. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20435002 Free PMC article.
-
The pituitary function of androgen receptor constitutes a glucocorticoid production circuit.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;27(13):4807-14. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02039-06. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17470551 Free PMC article.
-
Reflections on the diseases linked to mutations of the androgen receptor.Endocrine. 2005 Dec;28(3):243-62. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:28:3:243. Endocrine. 2005. PMID: 16388114 Review.
-
Orexin signaling in GABAergic lateral habenula neurons modulates aggressive behavior in male mice.Nat Neurosci. 2020 May;23(5):638-650. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0617-7. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Nat Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32284606 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

