Production of experimental malignant pleural effusions is dependent on invasion of the pleura and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor by human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 11106562
- PMCID: PMC1885766
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64828-6
Production of experimental malignant pleural effusions is dependent on invasion of the pleura and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor by human lung cancer cells
Abstract
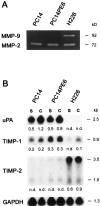
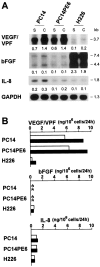
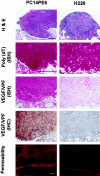
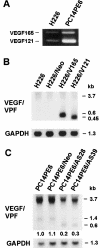
We determined the molecular mechanisms that regulate the pathogenesis of malignant pleural effusion (PE) associated with advanced stage of human, non-small-cell lung cancer. Intravenous injection of human PC14 and PC14PE6 (adenocarcinoma) or H226 (squamous cell carcinoma) cells into nude mice yielded numerous lung lesions. PC14 and PC14PE6 lung lesions invaded the pleura and produced PE containing a high level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-localized vascular hyperpermeability. Lung lesions produced by H226 cells were confined to the lung parenchyma with no PE. The level of expression of VEGF mRNA and protein by the cell lines directly correlated with extent of PE formation. Transfection of PC14PE6 cells with antisense VEGF165 gene did not inhibit invasion into the pleural space but reduced PE formation. H226 cells transfected with either sense VEGF 165 or sense VEGF 121 genes induced localized vascular hyperpermeability and produced PE only after direct implantation into the thoracic cavity. The production of PE was thus associated with the ability of tumor cells to invade the pleura, a property associated with expression of high levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and low levels of TIMP-2. Collectively, the data demonstrate that the production of malignant PE requires tumor cells to invade the pleura and express high levels of VEGF/VPF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment for malignant pleural effusion of human lung adenocarcinoma by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Mar;6(3):957-65. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10741721
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Anti-VEGF drugs compared with laser photocoagulation for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Dec 11:1-71. doi: 10.3310/PCGV5709. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39673354
-
The association of visceral pleural invasion with skip N2 metastasis on clinical stage IA NSCLC.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Mar 13;79:100334. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100334. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 38484584 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The angiogenetic pathway in malignant pleural effusions: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications.Exp Ther Med. 2010 Jan;1(1):3-7. doi: 10.3892/etm_00000001. Epub 2010 Jan 1. Exp Ther Med. 2010. PMID: 23136584 Free PMC article.
-
Pleural involvement in lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2015 Jun;7(6):1021-30. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.04.23. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 26150915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel orthotopic implantation model of human malignant pleural mesothelioma (EHMES-10 cells) highly expressing vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor.Cancer Sci. 2006 Mar;97(3):183-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00163.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16542214 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo imaging xenograft models for the evaluation of anti-brain tumor efficacy of targeted drugs.Cancer Med. 2017 Dec;6(12):2972-2983. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1255. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 29125233 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its role in oncogenesis of human gastric carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Aug;7(4):500-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i4.500. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landis SH, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA: Cancer statistics, CA. Cancer J Clin 1999, 49:8-64 - PubMed
-
- Mooi WJ: Common lung cancers. Hazleton PS eds. Spencer’s Pathology of the Lung. 1996, :pp 1009-1064 McGraw-Hill, New York
-
- Reed CE: Management of the malignant pleural effusion. Pass HI Mitchell JB Johnson DH Turrisi AT eds. Lung Cancer: Principles and Practice. 1996, :pp 643-654 Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
-
- Ruckdeschel JC: Management of malignant pleural effusions. Semin Oncol 1995, 22:58-63 - PubMed
-
- Sugiura S, Ando Y, Minami H, Ando M, Sakai S, Shimokata K: Prognostic value of pleural effusion in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1997, 3:47-50 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

