Neurobeachin: A protein kinase A-anchoring, beige/Chediak-higashi protein homolog implicated in neuronal membrane traffic
- PMID: 11102458
- PMCID: PMC6773050
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-23-08551.2000
Neurobeachin: A protein kinase A-anchoring, beige/Chediak-higashi protein homolog implicated in neuronal membrane traffic
Abstract
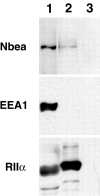
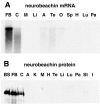
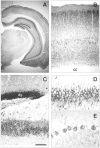
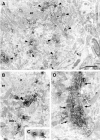
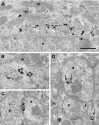
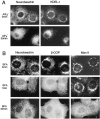
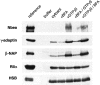
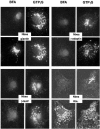
We describe the identification and initial characterization of neurobeachin, a neuron-specific multidomain protein of 327 kDa with a high-affinity binding site (K(d), 10 nm) for the type II regulatory subunit of protein kinase A (PKA RII). Neurobeachin is peripherally associated with pleomorphic tubulovesicular endomembranes near the trans sides of Golgi stacks and throughout the cell body and cell processes. It is also found in a subpopulation of synapses, where it is concentrated at the postsynaptic plasma membrane. In live cells, perinuclear neurobeachin is dispersed by brefeldin A (BFA) within 1 min, and in permeabilized cells a recruitment of neurobeachin from cytosol to Golgi-near membranes is stimulated by GTPgammaS and prevented by brefeldin A. Spots of neurobeachin recruitment are close to but distinct from recruitment sites of COP-I, AP-1, and AP-3 coat proteins involved in vesicle budding. These observations indicate that neurobeachin binding to membranes close to the trans-Golgi requires an ADP-ribosylation factor-like GTPase, possibly in association with a novel type of protein coat. A neurobeachin isoform that does not bind RII, beige-like protein (BGL), is expressed in many tissues. Neurobeachin, BGL, and approximately 10 other mammalian gene products share a characteristic C-terminal BEACH-WD40 sequence module, which is also present in gene products of invertebrates, plants, protozoans, and yeasts, thus defining a new protein family. The prototype member of this family of BEACH domain proteins, lysosomal trafficking regulator (LYST), is deficient in genetic defects of protein sorting in lysosome biogenesis (the beige mouse and Chediak-Higashi syndrome). Neurobeachin's subcellular localization, its coat protein-like membrane recruitment, and its sequence similarity to LYST suggest an involvement in neuronal post-Golgi membrane traffic, one of its functions being to recruit protein kinase A to the membranes with which it associates.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Trimeric G proteins modulate the dynamic interaction of PKAII with the Golgi complex.J Cell Sci. 1999 Nov;112 ( Pt 22):3869-78. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.22.3869. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10547348
-
Crystal structure of the PH-BEACH domains of human LRBA/BGL.Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 30;43(47):14873-80. doi: 10.1021/bi049498y. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15554694
-
ADP-Ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) regulates recruitment of the AP-3 adaptor complex to membranes.J Cell Biol. 1998 Jul 27;142(2):391-402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.2.391. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9679139 Free PMC article.
-
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome: a rare disorder of lysosomes and lysosome related organelles.Pigment Cell Res. 2002 Aug;15(4):251-7. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02038.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 12100490 Review.
-
The lysosomal trafficking regulator "LYST": an 80-year traffic jam.Front Immunol. 2024 May 7;15:1404846. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404846. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38774881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deleterious mutations in LRBA are associated with a syndrome of immune deficiency and autoimmunity.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Jun 8;90(6):986-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.04.015. Epub 2012 May 17. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22608502 Free PMC article.
-
Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng Mitigates Phenotypic Characteristics of Human Autism Spectrum Disorders in a Drosophila Melanogaster Rugose Mutant.Neurochem Res. 2021 Aug;46(8):1995-2007. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03337-7. Epub 2021 May 5. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33950474
-
The Possible Role of Neurobeachin in Extinction of Contextual Fear Memory.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 13;8(1):13752. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30589-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30213954 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron membrane trafficking and protein kinases involved in autism and ADHD.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 30;16(2):3095-115. doi: 10.3390/ijms16023095. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25647412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The WD repeat protein FAN regulates lysosome size independent from abnormal downregulation/membrane recruitment of protein kinase C.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jul 15;313(12):2703-18. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.04.020. Epub 2007 Apr 24. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17512928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam-Klages S, Adam D, Wiegmann K, Struve S, Kolanus W, Schneider-Mergener J, Krönke M. FAN, a novel WD-repeat protein, couples the p55 TNF-receptor to neutral sphingomyelinase. Cell. 1996;86:937–947. - PubMed
-
- Buechler YL, Herberg FW, Taylor SS. Regulation-defective mutants of type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:16495–16503. - PubMed
-
- Burack MA, Silverman MA, Banker G. The role of selective transport in neuronal protein sorting. Neuron. 2000;26:465–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
