Retinoblastoma protein disrupts interactions required for RNA polymerase III transcription
- PMID: 11094071
- PMCID: PMC102177
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9192-9202.2000
Retinoblastoma protein disrupts interactions required for RNA polymerase III transcription
Abstract
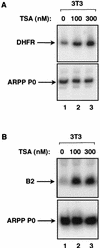
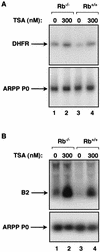
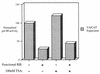
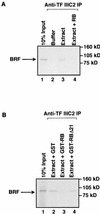
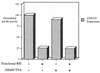
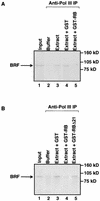
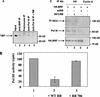
The retinoblastoma protein (RB) has been shown to suppress RNA polymerase (Pol) III transcription in vivo (R. J. White, D. Trouche, K. Martin, S. P. Jackson, and T. Kouzarides, Nature 382:88-90, 1996). This regulation involves interaction with TFIIIB, a multisubunit factor that is required for the expression of all Pol III templates (C. G. C. Larminie, C. A. Cairns, R. Mital, K. Martin, T. Kouzarides, S. P. Jackson, and R. J. White, EMBO J. 16:2061-2071, 1997; W.-M. Chu, Z. Wang, R. G. Roeder, and C. W. Schmid, J. Biol. Chem. 272:14755-14761, 1997). However, it has not been established why RB binding to TFIIIB results in transcriptional repression. For several Pol II-transcribed genes, RB has been shown to inhibit expression by recruiting histone deacetylases, which are thought to decrease promoter accessibility. We present evidence that histone deacetylases exert a negative effect on Pol III activity in vivo. However, RB remains able to regulate Pol III transcription in the presence of the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. Instead, RB represses by disrupting interactions between TFIIIB and other components of the basal Pol III transcription apparatus. Recruitment of TFIIIB to most class III genes requires its binding to TFIIIC2, but this can be blocked by RB. In addition, RB disrupts the interaction between TFIIIB and Pol III that is essential for transcription. The ability of RB to inhibit these key interactions can explain its action as a potent repressor of class III gene expression.
Figures

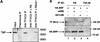
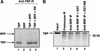
Similar articles
-
RNA polymerase III transcription factor IIIB is a target for repression by pocket proteins p107 and p130.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Jun;19(6):4255-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.6.4255. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10330166 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase III transcription repressed by Rb through its interactions with TFIIIB and TFIIIC2.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 6;272(23):14755-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.23.14755. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9169441
-
Mechanistic analysis of RNA polymerase III regulation by the retinoblastoma protein.EMBO J. 1997 Apr 15;16(8):2061-71. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.8.2061. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9155032 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase III repression by the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.09.011. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23063750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase III transcription: its control by tumor suppressors and its deregulation by transforming agents.Gene Expr. 2000;9(1-2):15-28. doi: 10.3727/000000001783992713. Gene Expr. 2000. PMID: 11097422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of human RNA polymerase III transcription by DNMT1 and DNMT3a DNA methyltransferases.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7039-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.285601. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22219193 Free PMC article.
-
A cyclin D2-Rb pathway regulates cardiac myocyte size and RNA polymerase III after biomechanical stress in adult myocardium.Circ Res. 2008 May 23;102(10):1222-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.163550. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18420946 Free PMC article.
-
p53 represses RNA polymerase III transcription by targeting TBP and inhibiting promoter occupancy by TFIIIB.EMBO J. 2003 Jun 2;22(11):2810-20. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg265. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12773395 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of TFIIIB during F9 cell differentiation.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 12;11:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-21. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20226026 Free PMC article.
-
RNF12 catalyzes BRF1 ubiquitination and regulates RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 4;294(1):130-141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004524. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30413534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzuherri H M, White R J. Regulation of a TATA-binding protein-associated factor during cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:17166–17171. - PubMed
-
- Brehm A, Kouzarides T. Retinoblastoma protein meets chromatin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:142–145. - PubMed
-
- Brehm A, Miska E A, McCance D J, Reid J L, Bannister A J, Kouzarides T. Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature. 1998;391:597–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
