Small molecule developmental screens reveal the logic and timing of vertebrate development
- PMID: 11087852
- PMCID: PMC27161
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.24.12965
Small molecule developmental screens reveal the logic and timing of vertebrate development
Abstract
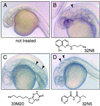
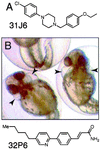
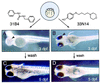
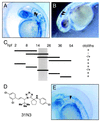
Much has been learned about vertebrate development by random mutagenesis followed by phenotypic screening and by targeted gene disruption followed by phenotypic analysis in model organisms. Because the timing of many developmental events is critical, it would be useful to have temporal control over modulation of gene function, a luxury frequently not possible with genetic mutants. Here, we demonstrate that small molecules capable of conditional gene product modulation can be identified through developmental screens in zebrafish. We have identified several small molecules that specifically modulate various aspects of vertebrate ontogeny, including development of the central nervous system, the cardiovascular system, the neural crest, and the ear. Several of the small molecules identified allowed us to dissect the logic of melanocyte and otolith development and to identify critical periods for these events. Small molecules identified in this way offer potential to dissect further these and other developmental processes and to identify novel genes involved in vertebrate development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simple vertebrate models for chemical genetics and drug discovery screens: lessons from zebrafish and Xenopus.Dev Dyn. 2009 Jun;238(6):1287-308. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21967. Dev Dyn. 2009. PMID: 19441060 Review.
-
Large scale genetics in a small vertebrate, the zebrafish.Int J Dev Biol. 1996 Feb;40(1):221-7. Int J Dev Biol. 1996. PMID: 8735932 Review.
-
Zebrafish genetics and vertebrate heart formation.Nat Rev Genet. 2001 Jan;2(1):39-48. doi: 10.1038/35047564. Nat Rev Genet. 2001. PMID: 11253067 Review.
-
Defining the boundaries of zebrafish developmental genetics.Nat Genet. 1996 Nov;14(3):258-63. doi: 10.1038/ng1196-258. Nat Genet. 1996. PMID: 8896553 Review.
-
Cloning of hif-1alpha and hif-2alpha and mRNA expression pattern during development in zebrafish.Gene Expr Patterns. 2007 Jan;7(3):339-45. doi: 10.1016/j.modgep.2006.08.002. Epub 2006 Aug 15. Gene Expr Patterns. 2007. PMID: 16997637
Cited by
-
Development and validation of an automated high-throughput system for zebrafish in vivo screenings.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036690. Epub 2012 May 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615792 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput screening for bioactive molecules using primary cell culture of transgenic zebrafish embryos.Cell Rep. 2012 Sep 27;2(3):695-704. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 22999940 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Novel Cancer Therapies Using Chemical Genetics and Zebrafish.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;916:103-24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-30654-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27165351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Juxtaposition of chemical and mutation-induced developmental defects in zebrafish reveal a copper-chelating activity for kalihinol F.Chem Biol. 2013 Jun 20;20(6):753-63. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.05.008. Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23790486 Free PMC article.
-
Microbead Implantation in the Zebrafish Embryo.J Vis Exp. 2015 Jul 30;(101):e52943. doi: 10.3791/52943. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26274386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaffield W, Incardona J P, Kapur R P, Roelink H. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1999;45:579–588. - PubMed
-
- Keeler R F. Teratology. 1970;3:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Eisen J S. Cell. 1996;87:969–977. - PubMed
-
- Haffter P, Granato M, Brand M, Mullins M C, Hammerschmidt M, Kane D A, Odenthal J, van Eeden F J, Jiang Y J, Heisenberg C P, et al. Development (Cambridge, UK) 1996;123:1–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

