Interactions of the PDZ-protein MAGI-1 with adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins
- PMID: 11077444
- PMCID: PMC3072458
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203906
Interactions of the PDZ-protein MAGI-1 with adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins
Abstract
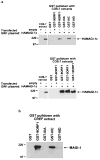
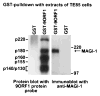
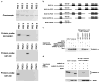
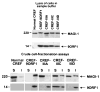
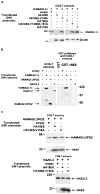
The oncoproteins of small DNA tumor viruses promote tumorigenesis by complexing with cellular factors intimately involved in the control of cell proliferation. The major oncogenic determinants for human adenovirus type 9 (Ad9) and high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV) are the E4-ORF1 and E6 proteins, respectively. These seemingly unrelated viral oncoproteins are similar in that their transforming activities in cells depend, in part, on a carboxyl-terminal PDZ domain-binding motif which mediates interactions with the cellular PDZ-protein DLG. Here we demonstrated that both Ad9 E4-ORF1 and high-risk HPV E6 proteins also bind to the DLG-related PDZ-protein MAGI-1. These interactions resulted in MAGI-1 being aberrantly sequestered in the cytoplasm by the Ad9 E4-ORF1 protein or being targeted for degradation by high-risk HPV E6 proteins. Transformation-defective mutant viral proteins, however, were deficient for these activities. Our findings indicate that MAGI-1 is a member of a select group of cellular PDZ proteins targeted by both adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk HPV E6 proteins and, in addition, suggest that the tumorigenic potentials of these viral oncoproteins depend, in part, on an ability to inhibit the function of MAGI-1 in cells.
Figures
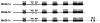





Similar articles
-
HPV E6 and MAGUK protein interactions: determination of the molecular basis for specific protein recognition and degradation.Oncogene. 2001 Sep 6;20(39):5431-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204719. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11571640 Free PMC article.
-
Link of the unique oncogenic properties of adenovirus type 9 E4-ORF1 to a select interaction with the candidate tumor suppressor protein ZO-2.EMBO J. 2001 Oct 15;20(20):5578-86. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5578. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11598001 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-PDZ domain protein MUPP1 is a cellular target for both adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus type 18 E6 oncoproteins.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(20):9680-93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9680-9693.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11000240 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity proteins: common targets for tumorigenic human viruses.Oncogene. 2008 Nov 24;27(55):7031-46. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.352. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19029943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus early E4 genes in viral oncogenesis.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 26;20(54):7847-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204914. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11753667 Review.
Cited by
-
HPV E6 and MAGUK protein interactions: determination of the molecular basis for specific protein recognition and degradation.Oncogene. 2001 Sep 6;20(39):5431-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204719. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11571640 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of apoptosis by human papillomavirus (HPV) oncoproteins.Arch Virol. 2006 Dec;151(12):2321-35. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0821-0. Epub 2006 Jul 27. Arch Virol. 2006. PMID: 16862386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus type 5 E1A and E6 proteins of low-risk cutaneous beta-human papillomaviruses suppress cell transformation through interaction with FOXK1/K2 transcription factors.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(6):2719-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02119-09. Epub 2010 Jan 6. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20053746 Free PMC article.
-
Selective PDZ protein-dependent stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by the adenovirus E4-ORF1 oncoprotein.Oncogene. 2003 Feb 6;22(5):710-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206151. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12569363 Free PMC article.
-
The Not-So-Good, the Bad and the Ugly: HPV E5, E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in the Orchestration of Carcinogenesis.Viruses. 2021 Sep 22;13(10):1892. doi: 10.3390/v13101892. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bosch FX, Manos MM, Munoz N, Sherman M, Jansen AM, Peto J, Schiffman MH, Moreno V, Kurman R, Shah KV. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;87:796–802. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Craven SE, Bredt DS. Cell. 1998;93:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Dobrosotskaya I, Guy RK, James GL. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31589–31597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

