Cathepsin B contributes to TNF-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis by promoting mitochondrial release of cytochrome c
- PMID: 11067865
- PMCID: PMC301415
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI9914
Cathepsin B contributes to TNF-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis by promoting mitochondrial release of cytochrome c
Abstract
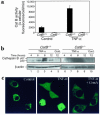
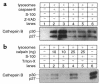
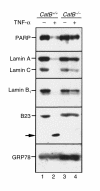
TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis is thought to involve mediators from acidic vesicles. Cathepsin B (cat B), a lysosomal cysteine protease, has recently been implicated in apoptosis. To determine whether cat B contributes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis, we exposed mouse hepatocytes to the cytokine in vitro and in vivo. Isolated hepatocytes treated with TNF-alpha in the presence of the transcription inhibitor actinomycin D (AcD) accumulated cat B in their cytosol. Further experiments using cell-free systems indicated that caspase-8 caused release of active cat B from purified lysosomes and that cat B, in turn, increased cytosol-induced release of cytochrome c from mitochondria. Consistent with these observations, the ability of TNF-alpha/AcD to induce mitochondrial release of cytochrome c, caspase activation, and apoptosis of isolated hepatocytes was markedly diminished in cells from CatB(-/-) mice. Deletion of the CatB gene resulted in diminished liver injury and enhanced survival after treatment in vivo with TNF-alpha and an adenovirus construct expressing the IkappaB superrepressor. Collectively, these observations suggest that caspase-mediated release of cat B from lysosomes enhances mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and subsequent caspase activation in TNF-alpha-treated hepatocytes.
Figures
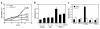
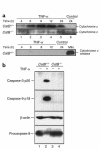


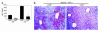
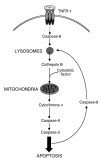
Comment in
-
A lysosomal protease enters the death scene.J Clin Invest. 2001 Jan;107(1):21-2. doi: 10.1172/JCI11829. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11134173 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cathepsin B knockout mice are resistant to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury: implications for therapeutic applications.Am J Pathol. 2001 Dec;159(6):2045-54. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63056-8. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11733355 Free PMC article.
-
Bid is upstream of lysosome-mediated caspase 2 activation in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced hepatocyte apoptosis.Gastroenterology. 2005 Jul;129(1):269-84. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.05.022. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 16012953
-
Nitric oxide prevents tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced rat hepatocyte apoptosis by the interruption of mitochondrial apoptotic signaling through S-nitrosylation of caspase-8.Hepatology. 2000 Oct;32(4 Pt 1):770-8. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.18291. Hepatology. 2000. PMID: 11003621
-
Dissection of the multiple mechanisms of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in liver injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2004 Oct-Dec;8(4):445-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2004.tb00469.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15601573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine regulation of liver injury and repair.Immunol Rev. 2000 Apr;174:160-71. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2002.017411.x. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10807515 Review.
Cited by
-
Cathepsin B maturation plays a critical role in leptin-induced hepatic cancer cell growth through activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes.Arch Pharm Res. 2023 Mar;46(3):160-176. doi: 10.1007/s12272-023-01437-2. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Arch Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 36905490
-
Deoxycholic acid (DCA) causes ligand-independent activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and FAS receptor in primary hepatocytes: inhibition of EGFR/mitogen-activated protein kinase-signaling module enhances DCA-induced apoptosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Sep;12(9):2629-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.9.2629. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11553704 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomes and Fas-mediated liver cell death.Biochem J. 2007 Apr 1;403(1):89-95. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061738. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17129211 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Cathepsin B in Peritoneal Fibrosis due to Peritoneal Dialysis.Int J Nephrol. 2019 Nov 13;2019:4150656. doi: 10.1155/2019/4150656. eCollection 2019. Int J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31815017 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of apoptosis-associated lysosomal membrane permeabilization.Apoptosis. 2010 May;15(5):527-40. doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0452-5. Apoptosis. 2010. PMID: 20077016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wallach D, et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:331–367. - PubMed
-
- McClain CJ, Cohen DA. Increased tumor necrosis factor production by monocytes in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1989;9:349–351. - PubMed
-
- Leist M, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis during the poisoning of mice with hepatotoxins. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:923–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

