Assessment of poliovirus eradication in Japan: genomic analysis of polioviruses isolated from river water and sewage in toyama prefecture
- PMID: 11055968
- PMCID: PMC92424
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.11.5087-5091.2000
Assessment of poliovirus eradication in Japan: genomic analysis of polioviruses isolated from river water and sewage in toyama prefecture
Abstract
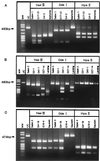
Seventy-eight poliovirus strains isolated from river water and sewage in Toyama Prefecture, Japan, during 1993 to 1995 were characterized by the PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method and by partially sequencing the VP3 and VP1 regions of the viral genome. Of these isolates, 36 were identified as Sabin vaccine strains, and 42 were identified as vaccine variant strains that had less than 1.4% nucleotide divergence from the Sabin strains, including 7 isolates with patterns different from those of Sabin strains as determined by PCR-RFLP analysis. These findings suggest that wild-type poliovirus was not circulating in Toyama Prefecture.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterisation of vaccine-derived polioviruses isolated from sewage and river water in Japan.Lancet. 2000 Oct 28;356(9240):1461-3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02868-3. Lancet. 2000. PMID: 11081527
-
Polioviruses with natural recombinant genomes isolated from vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis.Virology. 1993 Sep;196(1):199-208. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1468. Virology. 1993. PMID: 8102826
-
Sabin type 2 polioviruses with intertypic vaccine/vaccine recombinant genomes.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001 Nov;20(11):792-9. doi: 10.1007/s100960100610. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11783695
-
Isolation of vaccine-derived type 1 polioviruses displaying similar properties to virulent wild strain Mahoney from sewage in Japan.J Med Virol. 2002 Nov;68(3):445-51. doi: 10.1002/jmv.10224. J Med Virol. 2002. PMID: 12226835
-
Molecular evolution of oral poliovirus vaccine strains during multiplication in humans and possible implications for global eradication of poliovirus.Acta Virol. 2000 Apr;44(2):109-17. Acta Virol. 2000. PMID: 10989702 Review.
Cited by
-
Contextualizing Wastewater-Based surveillance in the COVID-19 vaccination era.Environ Int. 2023 Jan;171:107718. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107718. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Environ Int. 2023. PMID: 36584425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Longitudinal Survey for Genome-based Identification of SARS-CoV-2 in Sewage Water in Selected Lockdown Areas of Lahore City, Pakistan: A Potential Approach for Future Smart Lockdown Strategy.Biomed Environ Sci. 2021 Sep 20;34(9):729-733. doi: 10.3967/bes2021.101. Biomed Environ Sci. 2021. PMID: 34530963 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Wastewater surveillance for SARS-CoV-2: Lessons learnt from recent studies to define future applications.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Mar 10;759:143493. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143493. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33190883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental and air sampling are efficient methods for the detection and quantification of foot-and-mouth disease virus.J Virol Methods. 2021 Jan;287:113988. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.113988. Epub 2020 Oct 7. J Virol Methods. 2021. PMID: 33038353 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Most Commonly Used Methods for Sample Collection in Environmental Surveillance of Poliovirus.Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Oct 30;67(suppl_1):S90-S97. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy638. Clin Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30376094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander J P, Jr, Gary H E, Jr, Pallansch M A. Duration of poliovirus excretion and its implications for acute flaccid paralysis surveillance: a review of the literature. J Infect Dis. 1997;175(Suppl. 1):S176–S182. - PubMed
-
- Balanant J, Guillot S, Candrea A, Delpeyroux F, Crainic R. The natural genomic variability of poliovirus analyzed by a restriction fragment length polymorphism assay. Virology. 1991;184:645–654. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress toward global eradication of poliomyelitis, 1996. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:579–584. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress toward global eradication of poliomyelitis, 1997. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1998;47:414–419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

