High-mobility-group protein I can modulate binding of transcription factors to the U5 region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proviral promoter
- PMID: 11044097
- PMCID: PMC110927
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10523-10534.2000
High-mobility-group protein I can modulate binding of transcription factors to the U5 region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proviral promoter
Abstract
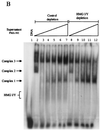
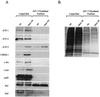
HMG I/Y appears to be a multifunctional protein that relies on in its ability to interact with DNA in a structure-specific manner and with DNA, binding transcriptional activators via distinct protein-protein interaction surfaces. To investigate the hypothesis that HMG I/Y may have a role in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) expression, we have analyzed whether HMG I/Y interacts with the 5' long terminal repeat and whether this interaction can modulate transcription factor binding. Using purified recombinant HMG I, we have identified several high-affinity binding sites which overlap important transcription factor binding sites. One of these HMG I binding sites coincides with an important binding site for AP-1 located downstream of the transcriptional start site, in the 5' untranslated region at the boundary of a positioned nucleosome. HMG I binding to this composite site inhibits the binding of recombinant AP-1. Consistent with this observation, using nuclear extracts prepared from Jurkat T cells, we show that HMG I (but not HMG Y) is strongly induced upon phorbol myristate acetate stimulation and this induced HMG I appears to both selectively inhibit the binding of basal DNA-binding proteins and enhance the binding of an inducible AP-1 transcription factor to this AP-1 binding site. We also report the novel finding that a component present in this inducible AP-1 complex is ATF-3. Taken together, these results argue that HMG I may play a fundamental role in HIV-1 expression by determining the nature of transcription factor-promoter interactions.
Figures
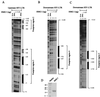

 R, start
site of transcription.
R, start
site of transcription.
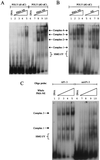
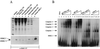

Similar articles
-
HMG I(Y) interferes with the DNA binding of NF-AT factors and the induction of the interleukin 4 promoter in T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Dec 24;93(26):15311-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.26.15311. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8986808 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of HMG-I(Y) imparts architectural specificity to a positioned nucleosome on the promoter of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha gene.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jul;20(13):4666-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.13.4666-4679.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10848593 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of a multipromoter gene. Selective 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate induction of a single transcription start site in the HMG-I/Y gene.J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14235-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14235. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7775485
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 transcription: role of the 5'-untranslated leader region (review).Int J Mol Med. 1998 May;1(5):875-81. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.1.5.875. Int J Mol Med. 1998. PMID: 9852310 Review.
-
The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is an essential structural component of a virus-inducible enhancer complex.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:73-81. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.011. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993. PMID: 7956090 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
HMGA1 directly interacts with TAR to modulate basal and Tat-dependent HIV transcription.RNA Biol. 2013 Mar;10(3):436-44. doi: 10.4161/rna.23686. Epub 2013 Feb 7. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23392246 Free PMC article.
-
HIC1 controls cellular- and HIV-1- gene transcription via interactions with CTIP2 and HMGA1.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 11;6:34920. doi: 10.1038/srep34920. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27725726 Free PMC article.
-
The Dual Roles of Activating Transcription Factor 3 (ATF3) in Inflammation, Apoptosis, Ferroptosis, and Pathogen Infection Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 9;25(2):824. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020824. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated self-inactivating lentiviral vectors produce full-length genomic transcripts competent for encapsidation and integration.J Virol. 2004 Aug;78(16):8421-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8421-8436.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15280451 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear functions of the HMG proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jan-Feb;1799(1-2):3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.09.001. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19748605 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Harthi L, Roebuck K A. Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 transcription: role of the 5′-untranslated leader region. Int J Mol Med. 1998;1:875–881. - PubMed
-
- Arlotta P, Rustighi A, Mantovani F, Manfioletti G, Giancotti V, Tell G, Damante G. High mobility group I proteins interfere with the homeodomains binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29904–29910. - PubMed
-
- Banks G C, Mohr B, Reeves R. The HMG-I(Y) A.T-hook peptide motif confers DNA-binding specificity to a structured chimeric protein. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:16536–16544. - PubMed
-
- Brown D A, Xu X, Nerenberg M. Genomic footprinting of HTLV type I and HIV type 1 in human T cell lines. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996;12:829–832. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

