Methylation of transcription factor binding sites in the Epstein-Barr virus latent cycle promoter Wp coincides with promoter down-regulation during virus-induced B-cell transformation
- PMID: 11044091
- PMCID: PMC110921
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10468-10479.2000
Methylation of transcription factor binding sites in the Epstein-Barr virus latent cycle promoter Wp coincides with promoter down-regulation during virus-induced B-cell transformation
Abstract
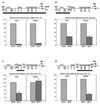
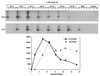
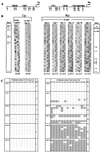
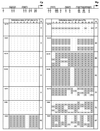
Two Epstein-Barr virus latent cycle promoters for nuclear antigen expression, Wp and Cp, are activated sequentially during virus-induced transformation of B cells to B lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) in vitro. Previously published restriction enzyme studies have indicated hypomethylation of CpG dinucleotides in the Wp and Cp regions of the viral genome in established LCLs, whereas these same regions appeared to be hypermethylated in Burkitt's lymphoma cells, where Wp and Cp are inactive. Here, using the more sensitive technique of bisulfite genomic sequencing, we reexamined the situation in established LCLs with the typical pattern of dominant Cp usage; surprisingly, this showed substantial methylation in the 400-bp regulatory region upstream of the Wp start site. This was not an artifact of long-term in vitro passage, since, in cultures of recently infected B cells, we found progressive methylation of Wp (but not Cp) regulatory sequences occurring between 7 and 21 days postinfection, coincident with the period in which dominant nuclear antigen promoter usage switches from Wp to Cp. Furthermore, in the equivalent in vivo situation, i.e., in the circulating B cells of acute infectious mononucleosis patients undergoing primary EBV infection, we again frequently observed selective methylation of Wp but not Cp sequences. An effector role for methylation in Wp silencing was supported by methylation cassette assays of Wp reporter constructs and by bandshift assays, where the binding of two sets of transcription factors important for Wp activation in B cells, BSAP/Pax5 and CREB/ATF proteins, was shown to be blocked by methylation of their binding sites.
Figures

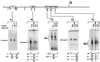
Similar articles
-
Methylation status of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BamHI W latent cycle promoter and promoter activity: analysis with novel EBV-positive Burkitt and lymphoblastoid cell lines.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(21):10700-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01204-06. Epub 2006 Aug 18. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16920819 Free PMC article.
-
Variable methylation of the Epstein-Barr virus Wp EBNA gene promoter in B-lymphoblastoid cell lines.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(24):14062-5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.14062-14065.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15564516 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus promoter initiating B-cell transformation is activated by RFX proteins and the B-cell-specific activator protein BSAP/Pax5.J Virol. 2000 Nov;74(22):10458-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10458-10467.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11044090 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of latent Epstein-Barr virus promoters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Mar-Apr;1799(3-4):228-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.10.005. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19853674 Review.
-
Host cell-dependent expression of latent Epstein-Barr virus genomes: regulation by DNA methylation.Adv Cancer Res. 2003;89:133-56. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(03)01004-2. Adv Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14587872 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence that direct inhibition of transcription factor binding is the prevailing mode of gene and repeat repression by DNA methylation.Nat Genet. 2022 Dec;54(12):1895-1906. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01241-6. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Nat Genet. 2022. PMID: 36471082 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle activator Zta interacts with methylated ZRE in the promoter of host target gene egr1.J Gen Virol. 2009 Jun;90(Pt 6):1450-1454. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.007922-0. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19264650 Free PMC article.
-
Burkitt's lymphoma: the Rosetta Stone deciphering Epstein-Barr virus biology.Semin Cancer Biol. 2009 Dec;19(6):377-88. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2009.07.004. Epub 2009 Jul 18. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009. PMID: 19619657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AP-1 homolog BZLF1 of Epstein-Barr virus has two essential functions dependent on the epigenetic state of the viral genome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 12;107(2):850-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911948107. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080764 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of varicella-zoster virus open reading frames 62 and 63 in latently infected human trigeminal ganglia.J Virol. 2006 May;80(10):4921-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.4921-4926.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16641283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfieri C, Birkenbach M, Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991;181:595–608. - PubMed
-
- Allday M J, Kundu D, Finerty S, Griffin B E. CpG methylation of viral DNA in EBV-associated tumours. Int J Cancer. 1990;45:1125–1130. - PubMed
-
- Babcock G J, Decker L L, Volk M, Thorley-Lawson D A. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity. 1998;9:395–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

