Different human TFIIIB activities direct RNA polymerase III transcription from TATA-containing and TATA-less promoters
- PMID: 11040218
- PMCID: PMC316990
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.836400
Different human TFIIIB activities direct RNA polymerase III transcription from TATA-containing and TATA-less promoters
Abstract
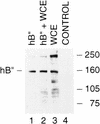
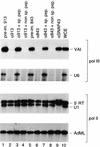
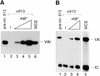
Transcription initiation at RNA polymerase III promoters requires transcription factor IIIB (TFIIIB), an activity that binds to RNA polymerase III promoters, generally through protein-protein contacts with DNA binding factors, and directly recruits RNA polymerase III. Saccharomyces cerevisiae TFIIIB is a complex of three subunits, TBP, the TFIIB-related factor BRF, and the more loosely associated polypeptide beta("). Although human homologs for two of the TFIIIB subunits, the TATA box-binding protein TBP and the TFIIB-related factor BRF, have been characterized, a human homolog of yeast B(") has not been described. Moreover, human BRF, unlike yeast BRF, is not universally required for RNA polymerase III transcription. In particular, it is not involved in transcription from the small nuclear RNA (snRNA)-type, TATA-containing, RNA polymerase III promoters. Here, we characterize two novel activities, a human homolog of yeast B("), which is required for transcription of both TATA-less and snRNA-type RNA polymerase III promoters, and a factor equally related to human BRF and TFIIB, designated BRFU, which is specifically required for transcription of snRNA-type RNA polymerase III promoters. Together, these results contribute to the definition of the basal RNA polymerase III transcription machinery and show that two types of TFIIIB activities, with specificities for different classes of RNA polymerase III promoters, have evolved in human cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Polymerase (Pol) III TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-associated factor Brf binds to a surface on TBP also required for activated Pol II transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1692-700. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1692. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9488486 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase III transcription from the human U6 and adenovirus type 2 VAI promoters has different requirements for human BRF, a subunit of human TFIIIB.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;16(12):7031-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.12.7031. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8943358 Free PMC article.
-
Alternatively spliced hBRF variants function at different RNA polymerase III promoters.EMBO J. 2000 Aug 1;19(15):4134-43. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.4134. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10921893 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the RNA polymerase III transcription machinery in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jul 1;29(13):2675-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2675. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11433012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase III. Genes, factors and transcriptional specificity.Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 15;212(1):1-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17626.x. Eur J Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8444147 Review.
Cited by
-
The p53 tumor suppressor protein represses human snRNA gene transcription by RNA polymerases II and III independently of sequence-specific DNA binding.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(8):3247-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3247-3260.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15798209 Free PMC article.
-
The fission yeast TFIIB-related factor limits RNA polymerase III to a TATA-dependent pathway of TBP recruitment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Apr 15;31(8):2108-16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg301. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12682361 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the inhibitory DNA-binding surface of human TATA-binding protein in recruitment of human TFIIB family members.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;23(22):8152-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8152-8160.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14585974 Free PMC article.
-
Brf1 loss and not overexpression disrupts tissues homeostasis in the intestine, liver and pancreas.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Dec;26(12):2535-2550. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0316-7. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30858608 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of the human TFIIB-related factor II protein reveals an essential role for the C-terminal domain in RNA polymerase III transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(21):9406-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9406-9418.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16227591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland R, Stewart AF, Gibson T. The SANT domain: A putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:87–88. - PubMed
-
- Bagby S, Kim S, Maldonado E, Tong KI, Reinberg D, Ikura M. Solution structure of the C-terminal core domain of human TFIIB: Similarity to cyclin A and interaction with TATA-binding protein. Cell. 1995;82:857–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
