AGO1, QDE-2, and RDE-1 are related proteins required for post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants, quelling in fungi, and RNA interference in animals
- PMID: 11016954
- PMCID: PMC17255
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.200217597
AGO1, QDE-2, and RDE-1 are related proteins required for post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants, quelling in fungi, and RNA interference in animals
Abstract
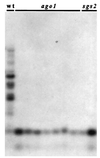
Introduction of transgene DNA may lead to specific degradation of RNAs that are homologous to the transgene transcribed sequence through phenomena named post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) in plants, quelling in fungi, and RNA interference (RNAi) in animals. It was shown previously that PTGS, quelling, and RNAi require a set of related proteins (SGS2, QDE-1, and EGO-1, respectively). Here we report the isolation of Arabidopsis mutants impaired in PTGS which are affected at the Argonaute1 (AGO1) locus. AGO1 is similar to QDE-2 required for quelling and RDE-1 required for RNAi. Sequencing of ago1 mutants revealed one amino acid essential for PTGS that is also present in QDE-2 and RDE-1 in a highly conserved motif. Taken together, these results confirm the hypothesis that these processes derive from a common ancestral mechanism that controls expression of invading nucleic acid molecules at the post-transcriptional level. As opposed to rde-1 and qde-2 mutants, which are viable, ago1 mutants display several developmental abnormalities, including sterility. These results raise the possibility that PTGS, or at least some of its elements, could participate in the regulation of gene expression during development in plants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fertile hypomorphic ARGONAUTE (ago1) mutants impaired in post-transcriptional gene silencing and virus resistance.Plant Cell. 2002 Mar;14(3):629-39. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010358. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 11910010 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis SGS2 and SGS3 genes are required for posttranscriptional gene silencing and natural virus resistance.Cell. 2000 May 26;101(5):533-42. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80863-6. Cell. 2000. PMID: 10850495
-
A branched pathway for transgene-induced RNA silencing in plants.Curr Biol. 2002 Apr 16;12(8):684-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00792-3. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 11967158
-
Post-transcriptional gene silencing mutants.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jun;43(2-3):275-84. doi: 10.1023/a:1006499832424. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10999410 Review.
-
Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants.J Cell Sci. 2001 Sep;114(Pt 17):3083-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.17.3083. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11590235 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges and Opportunities Arising from Host-Botrytis cinerea Interactions to Outline Novel and Sustainable Control Strategies: The Key Role of RNA Interference.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 20;25(12):6798. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126798. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potyviral silencing suppressor HCPro recruits and employs host ARGONAUTE1 in pro-viral functions.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Oct 8;16(10):e1008965. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008965. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33031436 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling in rice young panicle and vegetative organs and identification of panicle-specific genes through known gene functions.Mol Genet Genomics. 2005 Dec;274(5):467-76. doi: 10.1007/s00438-005-0043-2. Epub 2005 Oct 7. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16211393
-
SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 are required for juvenile development and the production of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis.Genes Dev. 2004 Oct 1;18(19):2368-79. doi: 10.1101/gad.1231804. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15466488 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing is inhibited by 3' non-coding sequences in Paramecium.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Nov 1;29(21):4387-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.21.4387. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11691926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baulcombe D C. Plant Mol Biol. 1996;34:125–137. - PubMed
-
- Depicker A, Van Montagu M. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:373–382. - PubMed
-
- Vaucheret H, Béclin C, Elmayan T, Feuerbach F, Godon C, Morel J-B, Mourrain P, Palauqui J-C, Vernhettes S. Plant J. 1998;16:651–659. - PubMed
-
- Kooter J M, Matzke M A, Meyer P. Trends Plant Sci. 1999;4:340–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

