Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice
- PMID: 11009421
- PMCID: PMC3582399
- DOI: 10.1126/science.289.5488.2350
Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice
Abstract
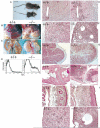
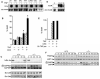
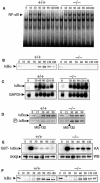
A20 is a cytoplasmic zinc finger protein that inhibits nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated programmed cell death (PCD). TNF dramatically increases A20 messenger RNA expression in all tissues. Mice deficient for A20 develop severe inflammation and cachexia, are hypersensitive to both lipopolysaccharide and TNF, and die prematurely. A20-deficient cells fail to terminate TNF-induced NF-kappaB responses. These cells are also more susceptible than control cells to undergo TNF-mediated PCD. Thus, A20 is critical for limiting inflammation by terminating TNF-induced NF-kappaB responses in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The zinc finger protein A20 inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by interfering with an RIP- or TRAF2-mediated transactivation signal and directly binds to a novel NF-kappaB-inhibiting protein ABIN.J Cell Biol. 1999 Jun 28;145(7):1471-82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.7.1471. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10385526 Free PMC article.
-
The seventh zinc finger motif of A20 is required for the suppression of TNF-α-induced apoptosis.FEBS Lett. 2015 May 22;589(12):1369-75. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 22. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 25911380
-
Combined expression of A1 and A20 achieves optimal protection of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.Kidney Int. 2005 Oct;68(4):1520-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00564.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16164629
-
ABINs: A20 binding inhibitors of NF-kappa B and apoptosis signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 15;78(2):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19464428 Review.
-
The biology of A20-binding inhibitors of NF-kappaB activation (ABINs).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;809:13-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0398-6_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25302363 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin E γ-Tocotrienol Inhibits Cytokine-Stimulated NF-κB Activation by Induction of Anti-Inflammatory A20 via Stress Adaptive Response Due to Modulation of Sphingolipids.J Immunol. 2015 Jul 1;195(1):126-33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403149. Epub 2015 May 22. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26002975 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome via Regulating the PPAR Gamma/NF-Kappa B Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jul 22;2020:4594631. doi: 10.1155/2020/4594631. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32774418 Free PMC article.
-
Cyld restrains the hyperactivation of synovial fibroblasts in inflammatory arthritis by regulating the TAK1/IKK2 signaling axis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 9;15(8):584. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06966-2. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39122678 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of SLE: functional relevance for monocytes/macrophages in disease.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:582352. doi: 10.1155/2012/582352. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23227085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitination and phosphorylation in the regulation of NOD2 signaling and NOD2-mediated disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov;1823(11):2022-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.03.017. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22522061 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

