A novel function for the tumor suppressor p16(INK4a): induction of anoikis via upregulation of the alpha(5)beta(1) fibronectin receptor
- PMID: 10995450
- PMCID: PMC2150704
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.1467
A novel function for the tumor suppressor p16(INK4a): induction of anoikis via upregulation of the alpha(5)beta(1) fibronectin receptor
Abstract
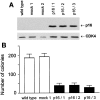
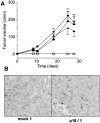
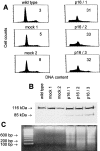
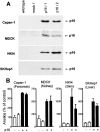
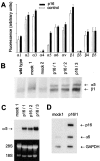
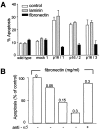
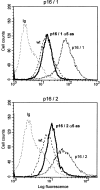
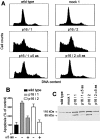
The tumor suppressor gene p16(INK4a) inhibits the kinase activity of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4-6/cyclin D complexes and subsequent phosphorylation of critical substrates necessary for transit through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Recent studies suggested that control of the G1/S boundary might not be the sole biological function of p16(INK4a). We hypothesized that p16(INK4a) might influence hitherto unknown critical features of a malignant epithelial phenotype, such as anchorage dependence. Here we provide evidence that stable transfection of p16(INK4a) restitutes apoptosis induction upon loss of anchorage (anoikis) in a variety of human cancer cells. Anoikis in p16(INK4a)-transfected cells was evidenced by DNA fragmentation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage upon cultivation on polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate-coated dishes and was associated with suppression of anchorage-independent growth as well as complete loss of tumorigenicity. p16(INK4a)-mediated anoikis was due to selective transcriptional upregulation of the alpha(5) integrin chain of the alpha(5)beta(1) fibronectin receptor as detected by FACS((R)) analysis, immunoprecipitation, Northern blotting, and nuclear run-on assays. Addition of soluble fibronectin and inhibitory alpha(5) antibodies to nonadherent cells completely abolished p16(INK4a)-mediated anoikis, whereas laminin was ineffective. Furthermore, antisense-induced downregulation of the alpha(5) integrin chain in p16(INK4a)-transfected cells restored resistance to anoikis. These data suggest a novel functional interference between a cell cycle-regulating tumor suppressor gene and membrane-bound integrins, thus regulating a hallmark feature of an epithelial transformed phenotype: susceptibility to anoikis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Growth inhibitory effect on glioma cells of adenovirus-mediated p16/INK4a gene transfer in vitro and in vivo.Int J Mol Med. 2000 Nov;6(5):559-63. Int J Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 11029524
-
Regulation of CDK7-carboxyl-terminal domain kinase activity by the tumor suppressor p16(INK4A) contributes to cell cycle regulation.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;20(20):7726-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.20.7726-7734.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11003668 Free PMC article.
-
G1/S cell cycle arrest provides anoikis resistance through Erk-mediated Bim suppression.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;25(12):5282-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.12.5282-5291.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15923641 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of pRb1-cyclin D1-cdk4/6-p16(INK4A) pathway in endometrial carcinogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2004 Jan 8;203(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2003.09.012. Cancer Lett. 2004. PMID: 14670612 Review.
-
Cancer cell cycles.Science. 1996 Dec 6;274(5293):1672-7. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1672. Science. 1996. PMID: 8939849 Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin-1 sensitizes carcinoma cells to anoikis via the fibronectin receptor α5β1-integrin.Cell Death Differ. 2011 May;18(5):806-16. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.148. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21113146 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in integrin expression modulates invasion of pancreatic cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 13;28(1):140. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-140. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19825166 Free PMC article.
-
Galectins: their network and roles in immunity/tumor growth control.Histochem Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;147(2):239-256. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1522-8. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28012132 Review.
-
Role of p16(INK4A) in Replicative Senescence and DNA Damage-Induced Premature Senescence in p53-Deficient Human Cells.Biochem Res Int. 2012;2012:951574. doi: 10.1155/2012/951574. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Biochem Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22924132 Free PMC article.
-
The fate of chemoresistance in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).BBA Clin. 2015 Mar 12;3:257-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2015.03.003. eCollection 2015 Jun. BBA Clin. 2015. PMID: 26676166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akiyama S.K., Olden K., Yamada K.M. Fibronectin and integrins in invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995;14:173–189. - PubMed
-
- Birkenmeier T.M., McQuillan J.J., Boedeker E.D., Argraves S., Ruoslahti E., Dean D.C. The α5β1 fibronectin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:20544–20549. - PubMed
-
- Bouvet M., Bold R.J., Lee J., Evans D.B., Abbruzzese J.L., Chiao P.J., McConkey D.J., Chandra J., Chada S., Fang B., Roth J.A. Adenovirus-mediated wild-type p53 tumor suppressor gene therapy induces apoptosis and suppresses growth of human pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 1998;5:681–688. - PubMed
-
- Bozzo C., Bellomo G., Silengo L., Tarone G., Altruda F. Soluble integrin ligands and growth factors independently rescue neuroblastoma cells from apoptosis under nonadherent conditions. Exp. Cell Res. 1997;23:326–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

