Cholate resistance in Lactococcus lactis is mediated by an ATP-dependent multispecific organic anion transporter
- PMID: 10960105
- PMCID: PMC94669
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.18.5196-5201.2000
Cholate resistance in Lactococcus lactis is mediated by an ATP-dependent multispecific organic anion transporter
Abstract
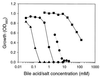
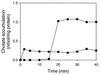
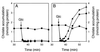
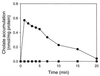
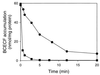
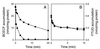
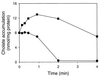
The cholate-resistant Lactococcus lactis strain C41-2, derived from wild-type L. lactis MG1363 through selection for growth on cholate-containing medium, displayed a reduced accumulation of cholate due to an enhanced active efflux. However, L. lactis C41-2 was not cross resistant to deoxycholate or cationic drugs, such as ethidium and rhodamine 6G, which are typical substrates of the multidrug transporters LmrP and LmrA in L. lactis MG1363. The cholate efflux activity in L. lactis C41-2 was not affected by the presence of valinomycin plus nigericin, which dissipated the proton motive force. In contrast, cholate efflux in L. lactis C41-2 was inhibited by ortho-vanadate, an inhibitor of P-type ATPases and ATP-binding cassette transporters. Besides ATP-dependent drug extrusion by LmrA, two other ATP-dependent efflux activities have previously been detected in L. lactis, one for the artificial pH probe 2',7'-bis-(2-carboxyethyl)-5(and 6)-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF) and the other for the artificial pH probe N-(fluorescein thio-ureanyl)-glutamate (FTUG). Surprisingly, the efflux rate of BCECF, but not that of FTUG, was significantly enhanced in L. lactis C41-2. Further experiments with L. lactis C41-2 cells and inside out membrane vesicles revealed that cholate and BCECF inhibit the transport of each other. These data demonstrate the role of an ATP-dependent multispecific organic anion transporter in cholate resistance in L. lactis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proton motive force-driven and ATP-dependent drug extrusion systems in multidrug-resistant Lactococcus lactis.J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(22):6957-64. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.22.6957-6964.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 7961458 Free PMC article.
-
The application of pH-sensitive fluorescent dyes in lactic acid bacteria reveals distinct extrusion systems for unmodified and conjugated dyes.Mol Membr Biol. 1996 Jul-Sep;13(3):173-81. doi: 10.3109/09687689609160594. Mol Membr Biol. 1996. PMID: 8905646
-
Proton motive force-dependent Hoechst 33342 transport by the ABC transporter LmrA of Lactococcus lactis.Biochemistry. 2005 Dec 27;44(51):16931-8. doi: 10.1021/bi051497y. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16363806
-
Structure-function analysis of multidrug transporters in Lactococcus lactis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Dec 6;1461(2):201-6. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(99)00172-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10581356 Review.
-
Molecular pharmacological characterization of two multidrug transporters in Lactococcus lactis.Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Mar;85(3):245-9. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(99)00057-1. Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 10739879 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholic acid is accumulated spontaneously, driven by membrane deltapH, in many lactobacilli.J Bacteriol. 2000 Nov;182(22):6525-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.22.6525-6528.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 11053402 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of Lactobacillus plantarum of Dairy-Product Origin for Probiotic Chèvre Cheese Production.Foods. 2022 Mar 24;11(7):934. doi: 10.3390/foods11070934. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35407020 Free PMC article.
-
The multidrug transporter LmrP protein mediates selective calcium efflux.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 10;287(33):27682-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.372334. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22730320 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of fructooligosaccharides by Lactobacillus paracasei 1195.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Apr;69(4):2217-22. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.2217-2222.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12676703 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation and response of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis to bile: a proteomic and physiological approach.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Nov;73(21):6757-67. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00637-07. Epub 2007 Sep 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17827318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolhuis H, van Veen H W, Brands J R, Putman M, Poolman B, Driessen A J M, Konings W N. Energetics and mechanism of drug transport mediated by the Lactococcal multidrug transporter LmrP. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24123–24128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

