Synergistic upregulation of interleukin-8 secretion from pulmonary epithelial cells by direct and monocyte-dependent effects of respiratory syncytial virus infection
- PMID: 10954542
- PMCID: PMC116353
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8425-8433.2000
Synergistic upregulation of interleukin-8 secretion from pulmonary epithelial cells by direct and monocyte-dependent effects of respiratory syncytial virus infection
Abstract
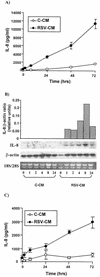
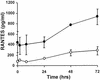
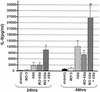
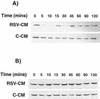
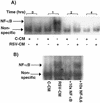
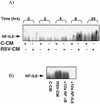
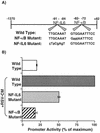
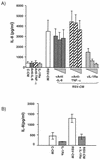
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection is the major cause of severe bronchiolitis in infants. Pathology of this infection is partly due to excessive proinflammatory leukocyte influx mediated by chemokines. Although direct infection of the respiratory epithelium by RSV may induce chemokine secretion, little is known about the role of cytokine networks. We investigated the effects of conditioned medium (CM) from RSV-infected monocytes (RSV-CM) on respiratory epithelial (A549) cell chemokine release. RSV-CM, but not control CM (both at a 1:5 dilution), stimulated interleukin-8 (IL-8) secretion from A549 cells within 2 h, and secretion increased over 72 h to 11,360 +/- 1,090 pg/ml without affecting cell viability. In contrast, RSV-CM had only a small effect on RANTES secretion. RSV-CM interacted with direct RSV infection to synergistically amplify IL-8 secretion from respiratory epithelial cells (levels of secretion at 48 h were as follows: RSV-CM alone, 8,140 +/- 2,160 pg/ml; RSV alone, 12,170 +/- 300 pg/ml; RSV-CM plus RSV, 27,040 +/- 5,260 pg/ml; P < 0.05). RSV-CM induced degradation of IkappaBalpha within 5 min but did not affect IkappaBbeta. RSV-CM activated transient nuclear binding of NF-kappaB within 1 h, while activation of NF-IL6 was delayed until 8 h and was still detectable at 24 h. Promoter-reporter analysis demonstrated that NF-kappaB binding was essential and that NF-IL6 was important for IL-8 promoter activity in RSV-CM-activated cells. Blocking experiments revealed that the effects of RSV-CM depended on monocyte-derived IL-1 but that tumor necrosis factor alpha was not involved in this network. In summary, RSV infection of monocytes results in and amplifies direct RSV-mediated IL-8 secretion from respiratory epithelial cells by an NF-kappaB-dependent, NF-IL6-requiring mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pulmonary epithelial cells are a source of IL-8 in the response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: essential role of IL-1 from infected monocytes in a NF-kappa B-dependent network.J Immunol. 1999 Oct 1;163(7):3936-47. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10490995
-
Respiratory syncytial virus-induced RANTES production from human bronchial epithelial cells is dependent on nuclear factor-kappa B nuclear binding and is inhibited by adenovirus-mediated expression of inhibitor of kappa B alpha.J Immunol. 1998 Jul 15;161(2):1007-16. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9670982
-
Interleukin-8, interleukin-6, and soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor type I release from a human pulmonary epithelial cell line (A549) exposed to respiratory syncytial virus.Immunology. 1994 May;82(1):126-33. Immunology. 1994. PMID: 7519169 Free PMC article.
-
RSV-infected airway epithelial cells cause biphasic up-regulation of CCR1 expression on human monocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2007 Jun;81(6):1487-95. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1006611. Epub 2007 Mar 27. J Leukoc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17389578
-
Airway Epithelial Derived Cytokines and Chemokines and Their Role in the Immune Response to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.Pathogens. 2019 Jul 19;8(3):106. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8030106. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31331089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Actin- and clathrin-dependent mechanisms regulate interferon gamma release after stimulation of human immune cells with respiratory syncytial virus.Virol J. 2016 Mar 22;13:52. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0506-6. Virol J. 2016. PMID: 27004689 Free PMC article.
-
Human beta defensin-3 mediated activation of β-catenin during human respiratory syncytial virus infection: interaction of HBD3 with LDL receptor-related protein 5.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1186510. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1186510. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37426017 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced clearance of respiratory syncytial virus infection in a preterm lamb model.Microbes Infect. 2004 Nov;6(14):1312-9. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2004.08.006. Microbes Infect. 2004. PMID: 15555538 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of global gene expression changes in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to spores of the allergenic fungus, Alternaria alternata.Front Microbiol. 2013 Jul 19;4:196. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00196. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23882263 Free PMC article.
-
Oxymetazoline modulates proinflammatory cytokines and the T-cell stimulatory capacity of dendritic cells.Exp Dermatol. 2007 Mar;16(3):171-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2006.00527.x. Exp Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17286808 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

