Increased ICAM-1 expression in transformed human oral epithelial cells: molecular mechanism and functional role in peripheral blood mononuclear cell adhesion and lymphokine-activated-killer cell cytotoxicity
- PMID: 10938387
- PMCID: PMC3513339
Increased ICAM-1 expression in transformed human oral epithelial cells: molecular mechanism and functional role in peripheral blood mononuclear cell adhesion and lymphokine-activated-killer cell cytotoxicity
Abstract
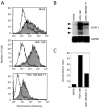
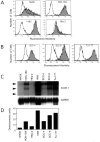
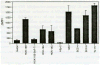
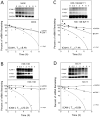
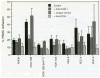
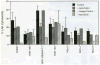
The intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1, CD54) serves as a counter-receptor for the beta2-integrins, LFA-1 and Mac-1, which are expressed on leukocytes. Although expression of ICAM-1 on tumor cells has a role in tumor progression and development, information on ICAM-1 expression and its role in oral cancer has not been established. Normal human oral keratinocytes (NHOK), human papilloma virus (HPV)-immortalized human oral keratinocyte lines (HOK-16B, HOK-18A, and HOK-18C), and six human oral neoplastic cell lines (HOK-16B-BaP-T1, SCC-4, SCC-9, HEp-2, Tu-177 and 1483) were used to study ICAM-1 expression and its functional role in vitro. Our results demonstrated that NHOK express negligible levels of ICAM-1, whereas immortalized human oral keratinocytes and cancer cells express significantly higher levels of ICAM-1, except for HOK-16B-BaP-T1 and HEp-2. Altered mRNA half-lives did not fully account for the increased accumulation of ICAM-1 mRNA. Adhesion of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to epithelial cells correlated with cell surface ICAM-1 expression levels. This adhesion was inhibited by antibodies specific for either ICAM-1 or LFA-1/Mac-1, suggesting a role for these molecules in adhesion. In contrast, lymphokine-activated-killer (LAK) cell cytotoxic killing of epithelial cells did not correlate with ICAM-1 levels or with adhesion. Nonetheless, within each cell line, blocking of ICAM-1 or LFA-1/Mac-1 reduced LAK cell killing, suggesting that ICAM-1 is involved in mediating this killing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different susceptibility of cervical keratinocytes containing human papillomavirus to cell-mediated cytotoxicity.Chin Med J (Engl). 1996 Nov;109(11):854-8. Chin Med J (Engl). 1996. PMID: 9275369
-
Role of adhesion molecules in lymphokine-activated killer cell killing of bladder cancer cells: further evidence for a third ligand for leucocyte function-associated antigen-1.Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):286-91. Immunology. 1992. PMID: 1353063 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-associated lymphotoxin-expressing lymphokine-activated killer cells up-regulate intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on target tumor cells in vitro.Cell Immunol. 1995 Aug;164(1):119-25. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1150. Cell Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7634343
-
Both HPV and carcinogen contribute to the development of resistance to apoptosis during oral carcinogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2000 Mar;16(3):591-7. doi: 10.3892/ijo.16.3.591. Int J Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10675494
-
ICAM-1 expression by lung cancer cell lines: effects of upregulation by cytokines on the interaction with LAK cells.Eur Respir J. 1996 Sep;9(9):1831-8. doi: 10.1183/09031936.96.09091831. Eur Respir J. 1996. PMID: 8880099
Cited by
-
Enhancement of Programmed Death Ligand 2 on Hepatitis C Virus Infected Hepatocytes by Calcineurin Inhibitors.Transplantation. 2015 Jul;99(7):1447-54. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000572. Transplantation. 2015. PMID: 25675203 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Integrin Overexpression as a Model of Murine Autoimmunity.Biol Proced Online. 2003;5:211-221. doi: 10.1251/bpo64. Epub 2003 Oct 24. Biol Proced Online. 2003. PMID: 14615818 Free PMC article.
-
Capacity of human beta-defensin expression in gene-transduced and cytokine-induced cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Jan 6;339(1):344-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.020. Epub 2005 Nov 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16298338 Free PMC article.
-
Poly I:C-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in intestinal epithelial cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 May;156(2):294-302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03892.x. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19284409 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1-dependent activation of interleukin 8 expression in Candida albicans-infected human gingival epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2005 Jan;73(1):622-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.622-626.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15618204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marlin SD, Springer TA. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) Cell. 1987;51:813–819. - PubMed
-
- Rosenstein Y, Park JK, Hahn WC, Rosen FS, Bierer BE, Burakoff SJ. CD43, a molecule defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, binds ICAM-1. Nature. 1991;354:233–235. - PubMed
-
- Dustin ML, Rothlein R, Bhan AK, Dinarello CA, Springer TA. Induction by IL-1 and interferon-γ: tissue distribution, biochemistry and function of an adherence molecule (ICAM-1) J Immunol. 1986;137:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Kashihara-Sawami M, Norris D. The state of differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes determines the level of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression induced by γ-interferon. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;98:741–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

