Apoptosis
- PMID: 10889903
- PMCID: PMC1186906
- DOI: 10.1136/mp.53.2.55
Apoptosis
Abstract
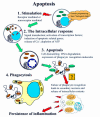
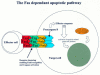
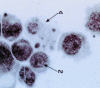
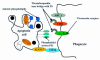
Apoptosis is the genetically regulated form of cell death that permits the safe disposal of cells at the point in time when they have fulfilled their intended biological function. Examples of apoptosis can be cited throughout the whole of the animal and plant kingdoms. It is a vitally important process during normal development and the adult life of many living organisms. In humans, dysregulation of apoptosis can result in inflammatory, malignant, autoimmune, and neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, infectious agents, including viruses, exploit cellular apoptosis in the host to evade the immune system. This review gives a brief historical perspective of some of the landmark discoveries in apoptosis research. The morphological and biochemical stages of apoptosis are then covered, followed by an overview of how it can be studied in the laboratory. Finally, the implications for therapeutic intervention in disease treatment are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-function analysis of an evolutionary conserved protein, DAP3, which mediates TNF-alpha- and Fas-induced cell death.EMBO J. 1999 Jan 15;18(2):353-62. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.2.353. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 9889192 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis-modulating agents in combination with radiotherapy-current status and outlook.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Feb 1;58(2):542-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.067. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14751526 Review.
-
Teaching resources. Apoptosis.Sci STKE. 2005 May 24;2005(285):tr16. doi: 10.1126/stke.2852005tr16. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 15914728
-
Functional genomics in sarcoidosis--reduced or increased apoptosis?Swiss Med Wkly. 2001 Aug 11;131(31-32):459-70. doi: 10.4414/smw.2001.09808. Swiss Med Wkly. 2001. PMID: 11641969
-
The Bcl-2 protein family: sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions.Mol Immunol. 2003 Jan;39(11):615-47. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00252-3. Mol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12493639 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptotic microtubules delimit an active caspase free area in the cellular cortex during the execution phase of apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Mar 7;4(3):e527. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.58. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23470534 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of genes involved in hybrid lethality in hybrid tobacco cells (Nicotiana suaveolens x N. tabacum) using suppression subtractive hybridization.Plant Cell Rep. 2007 Sep;26(9):1595-604. doi: 10.1007/s00299-007-0352-5. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Plant Cell Rep. 2007. PMID: 17410367
-
Axotomy-induced neurotrophic withdrawal causes the loss of phenotypic differentiation and downregulation of NGF signalling, but not death of septal cholinergic neurons.Mol Neurodegener. 2010 Jan 19;5:5. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2010. PMID: 20205865 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of apoptotic cells: generation of zombie cells.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Aug 14;5(8):e1369. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.332. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25118929 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs in apoptosis: identification and function.Turk J Biol. 2021 Nov 14;46(1):1-40. doi: 10.3906/biy-2109-35. eCollection 2022. Turk J Biol. 2021. PMID: 37533667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Virchow R, Chandler AB, eds. Cellular pathology as based upon physiological and pathological histology. New York: Dover Publications, 1859. - PubMed
-
- Weigert C. Uber Croup und Diptheritis. Ein experimenteller und anatomischer Beitrag zur Pathologie der specifischen Entzundungsformen. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 1877;72:461–501.
-
- Flemming W. Uber die bildung von richtungsfiguren in saugethiereiern beim untergang graaf'scher follikel. Arch Anat Entwgesch 1885:221–4.
-
- Graper L. Eine neue Anschauung uber physiologische Zellausschaltung. Archive Zellforsch 1914;12:373–94.
-
- Glucksmann A. Cell deaths in normal vertebrate ontogeny. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 1951;26:59–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
