Glucagon-like peptide-2 enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function of both transcellular and paracellular pathways in the mouse
- PMID: 10861272
- PMCID: PMC1727982
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.47.1.112
Glucagon-like peptide-2 enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function of both transcellular and paracellular pathways in the mouse
Abstract
Background and aims: Glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP-2) is a recently identified potent intestinotrophic factor. We have evaluated the effect of GLP-2 treatment on intestinal epithelial barrier function in mice.
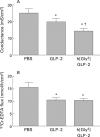
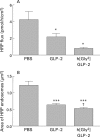
Methods: CD-1 mice were injected subcutaneously with GLP-2 or a protease resistant analogue, h[Gly(2)]GLP-2, twice daily for up to 10 days. Saline injected mice served as controls. Jejunal segments were mounted in Ussing chambers. Tissue conductance was measured and unidirectional fluxes were determined for (i) Na(+) and the small inert probe Cr-EDTA (both transported via the paracellular pathway) and (ii) the macromolecule horseradish peroxidase (HRP, transported via the transcellular pathway).
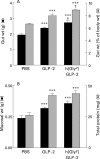
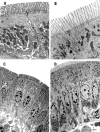
Results: Mice treated with GLP-2 or h[Gly(2)]GLP-2 for 10 days demonstrated significantly reduced intestinal conductance and fluxes of Na(+), Cr-EDTA, and HRP. Electron microscopy confirmed that GLP-2 reduced endocytic uptake of HRP into enterocytes. Functional changes (evident by four hours) preceded morphological changes (evident by 48 hours).
Conclusions: GLP-2 enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function by affecting both paracellular and transcellular pathways and thus may be of therapeutic value in a number of gastrointestinal conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enteroendocrine-derived glucagon-like peptide-2 controls intestinal amino acid transport.Mol Metab. 2017 Jan 17;6(3):245-255. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.01.005. eCollection 2017 Mar. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28271031 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal paracellular permeability during malnutrition in guinea pigs: effect of high dietary zinc.Gut. 1996 Sep;39(3):416-22. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.3.416. Gut. 1996. PMID: 8949647 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide 2 enhances intestinal epithelial restitution.J Surg Res. 2002 Sep;107(1):44-9. doi: 10.1006/jsre.2002.6504. J Surg Res. 2002. PMID: 12384063
-
Gut hormones, and short bowel syndrome: the enigmatic role of glucagon-like peptide-2 in the regulation of intestinal adaptation.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jul 14;12(26):4117-29. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4117. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16830359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal permeation enhancers: Lessons learned from studies using an organ culture model.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021 Jan 1;1863(1):183474. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183474. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 32946886 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Gut-Derived Secretory Factors in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Their Possible Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 8;19(10):3064. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103064. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30297626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Present and Future Therapeutic Approaches to Barrier Dysfunction.Front Nutr. 2021 Oct 28;8:718093. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.718093. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34778332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Design of Potent and Selective d-Peptide Agonists of the Glucagon-like Peptide-2 Receptor.J Med Chem. 2023 Aug 10;66(15):10342-10353. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00464. Epub 2023 Jul 25. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37491005 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling protein 2 involved in protection of glucagon-like peptide 2 in small intestine with ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.Dig Dis Sci. 2005 Mar;50(3):554-60. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-2474-3. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15810642
-
The roles of glucagon-like peptide-2 and the intestinal epithelial insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in regulating microvillus length.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 10;9(1):13010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49510-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31506583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
