The condensin complex governs chromosome condensation and mitotic transmission of rDNA
- PMID: 10811823
- PMCID: PMC2174567
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.4.811
The condensin complex governs chromosome condensation and mitotic transmission of rDNA
Abstract
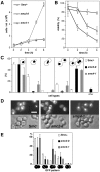
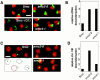
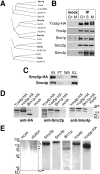
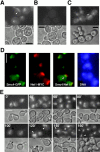
We have characterized five genes encoding condensin components in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. All genes are essential for cell viability and encode proteins that form a complex in vivo. We characterized new mutant alleles of the genes encoding the core subunits of this complex, smc2-8 and smc4-1. Both SMC2 and SMC4 are essential for chromosome transmission in anaphase. Mutations in these genes cause defects in establishing condensation of unique (chromosome VIII arm) and repetitive (rDNA) regions of the genome but do not impair sister chromatid cohesion. In vivo localization of Smc4p fused to green fluorescent protein showed that, unexpectedly, in S. cerevisiae the condensin complex concentrates in the rDNA region at the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. rDNA segregation in mitosis is delayed and/or stalled in smc2 and smc4 mutants, compared with separation of pericentromeric and distal arm regions. Mitotic transmission of chromosome III carrying the rDNA translocation is impaired in smc2 and smc4 mutants. Thus, the condensin complex in S. cerevisiae has a specialized function in mitotic segregation of the rDNA locus. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis revealed that condensin is physically associated with rDNA in vivo. Thus, the rDNA array is the first identified set of DNA sequences specifically bound by condensin in vivo. The biological role of higher-order chromosome structure in S. cerevisiae is discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cdc14p/FEAR pathway controls segregation of nucleolus in S. cerevisiae by facilitating condensin targeting to rDNA chromatin in anaphase.Cell Cycle. 2004 Jul;3(7):960-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.3.7.1003. Epub 2004 Jul 4. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15190202 Free PMC article.
-
Condensin-dependent rDNA decatenation introduces a temporal pattern to chromosome segregation.Curr Biol. 2008 Jul 22;18(14):1084-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.06.058. Curr Biol. 2008. PMID: 18635352
-
Cell cycle-dependent kinetochore localization of condensin complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Struct Biol. 2008 May;162(2):248-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2008.01.002. Epub 2008 Jan 11. J Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18296067
-
Deciphering condensin action during chromosome segregation.Trends Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;21(9):552-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Trends Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21763138 Review.
-
A case of selfish nucleolar segregation.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jan;4(1):113-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.1.1488. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15655374 Review.
Cited by
-
Repression of essential cell cycle genes increases cellular fitness.PLoS Genet. 2022 Aug 29;18(8):e1010349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010349. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36037231 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of Ycg1 Limit Condensin Function during the Cell Cycle.PLoS Genet. 2016 Jul 27;12(7):e1006216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006216. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27463097 Free PMC article.
-
Condensin dysfunction in human cells induces nonrandom chromosomal breaks in anaphase, with distinct patterns for both unique and repeated genomic regions.Chromosoma. 2012 Apr;121(2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s00412-011-0353-6. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Chromosoma. 2012. PMID: 22179743
-
Essential global role of CDC14 in DNA synthesis revealed by chromosome underreplication unrecognized by checkpoints in cdc14 mutants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 25;106(34):14466-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900190106. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19666479 Free PMC article.
-
Sir2p exists in two nucleosome-binding complexes with distinct deacetylase activities.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 15;20(16):4522-35. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4522. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11500379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat M.A., Philp A.V., Glover D.M., Bellen H.J. Chromatid segregation at anaphase requires the barren product, a novel chromosome-associated protein that interacts with Topoisomerase II. Cell. 1996;87:1103–1114. - PubMed
-
- Bryk M., Banerjee M., Murphy M., Knudsen K.E., Garfinkel D.J., Curcio M.J. Transcriptional silencing of Ty1 elements in the RDN1 locus of yeast. Genes Dev. 1997;11:255–269. - PubMed
-
- Chuang P., Albertson D., Meyer B. DPY-27a chromosome condensation protein homolog that regulates C. elegans dosage compensation through association with the X chromosome. Cell. 1994;79:459–474. - PubMed
-
- Chuang P.T., Lieb J.D., Meyer B.J. Sex-specific assembly of a dosage compensation complex on the nematode X chromosome. Science. 1996;274:1736–1739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

