Cuneiform neurons activated during cholinergically induced active sleep in the cat
- PMID: 10777795
- PMCID: PMC6773137
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-09-03319.2000
Cuneiform neurons activated during cholinergically induced active sleep in the cat
Abstract
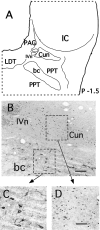
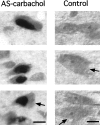
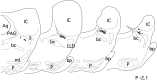
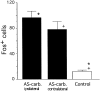
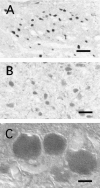
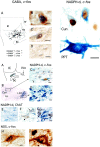
In the present study, we report that the cuneiform (Cun) nucleus, a brainstem structure that before now has not been implicated in sleep processes, exhibits a large number of neurons that express c-fos during carbachol-induced active sleep (AS-carbachol). Compared with control (awake) cats, during AS-carbachol, there was a 671% increase in the number of neurons that expressed c-fos in this structure. Within the Cun nucleus, three immunocytochemically distinct populations of neurons were observed. One group consisted of GABAergic neurons, which predominantly did not express c-fos during AS-carbachol. Two other different populations expressed c-fos during this state. One of the Fos-positive (Fos(+)) populations consisted of a distinct group of nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-NADPH-diaphorase (NADPH-d)-containing neurons; the neurotransmitter of the other Fos(+) population remains unknown. The Cun nucleus did not contain cholinergic, catecholaminergic, serotonergic, or glycinergic neurons. On the basis of neuronal activation during AS-carbachol, as indicated by c-fos expression, we suggest that the Cun nucleus is involved, in an as yet unknown manner, in the physiological expression of active sleep. The finding of a population of NOS-NADPH-d containing neurons, which were activated during AS-carbachol, suggests that nitrergic modulation of their target cell groups is likely to play a role in active sleep-related physiological processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GABAergic neurons of the cat dorsal raphe nucleus express c-fos during carbachol-induced active sleep.Brain Res. 2000 Nov 24;884(1--2):68-76. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02891-2. Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11082488
-
Gudden's dorsal tegmental nucleus is activated in carbachol-induced active (REM) sleep and active wakefulness.Brain Res. 2002 Jul 19;944(1-2):184-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02561-1. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12106678
-
c-fos Expression in mesopontine noradrenergic and cholinergic neurons of the cat during carbachol-induced active sleep: a double-labeling study.Sleep Res Online. 1998;1(1):28-40. Sleep Res Online. 1998. PMID: 11382855
-
Carbachol models of REM sleep: recent developments and new directions.Arch Ital Biol. 2001 Feb;139(1-2):147-68. Arch Ital Biol. 2001. PMID: 11256182 Review.
-
Hypothalamic control of sleep.Sleep Med. 2007 Jun;8(4):291-301. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2007.03.013. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Sleep Med. 2007. PMID: 17468047 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological and electrophysiological properties of serotonin neurons with NMDA modulation in the mesencephalic locomotor region of neonatal ePet-EYFP mice.Exp Brain Res. 2019 Dec;237(12):3333-3350. doi: 10.1007/s00221-019-05675-z. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Exp Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31720812
-
Involvement of the 5-HT1A receptor of the cuneiform nucleus in the regulation of cardiovascular responses during normal and hemorrhagic conditions.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Jul;23(7):858-864. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.40453.9579. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32774806 Free PMC article.
-
The nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-Nitro-L-arginine increases basal forebrain acetylcholine release during sleep and wakefulness.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 1;22(13):5597-605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05597.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12097511 Free PMC article.
-
Human TRPV1 is an efficient thermogenetic actuator for chronic neuromodulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 25;81(1):437. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05475-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39448456 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem neural mechanisms controlling locomotion with special reference to basal vertebrates.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Mar 30;17:910207. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.910207. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 37063386 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Appell PP, Behan M. Sources of subcortical GABAergic projections to the superior colliculus in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1990;302:143–158. - PubMed
-
- Baghdoyan HA, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, McCarley RW, Hobson JA. A neuroanatomical gradient in the pontine tegmentum for the cholinoceptive induction of desynchronized sleep signs. Brain Res. 1987;414:245–261. - PubMed
-
- Baghdoyan HA, Lydic R, Callaway CW, Hobson JA. The carbachol-induced enhancement of desynchronized sleep is dose dependent and antagonized by centrally administered atropine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1989;2:67–69. - PubMed
-
- Beart PM, Summers RJ, Stephenson JA, Cook CJ, Christie MJ. Excitatory aminoacid projections to the periaqueductal gray in the rat: a retrograde transport study utilizing d[3H]aspartate and [3H]GABA. Neuroscience. 1990;34:163–176. - PubMed
-
- Beitz AJ. The nuclei of origin of brain stem enkephalin and substance P projections to the rodent nucleus raphe magnus. Neuroscience. 1982;7:2753–2768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
