The galE gene of Campylobacter jejuni is involved in lipopolysaccharide synthesis and virulence
- PMID: 10768949
- PMCID: PMC97464
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2594-2601.2000
The galE gene of Campylobacter jejuni is involved in lipopolysaccharide synthesis and virulence
Abstract
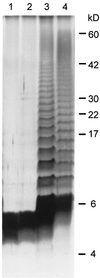
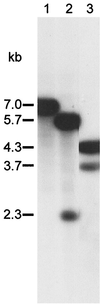
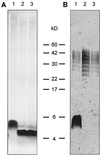
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is one of the main virulence factors of gram-negative bacteria. The LPS from Campylobacter spp. has endotoxic properties and has been shown to play a role in adhesion. We previously cloned a gene cluster (wla) which is involved in the synthesis of the Campylobacter jejuni 81116 LPS molecule. Sequence alignment of the first gene in this cluster indicated similarity with galE genes. These genes encode a UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, which catalyzes the interconversion of UDP-galactose and UDP-glucose. A Salmonella galE mutant was transformed with the galE gene from C. jejuni. The LPS analysis of wild-type, galE, and complemented galE Salmonella strains showed that the C. jejuni galE gene could restore the smooth wild-type Salmonella LPS. A UDP-glucose 4-epimerase assay was used to demonstrate that the galE gene from C. jejuni encoded this epimerase. We constructed a C. jejuni galE mutant which expressed a lipid A-core molecule of reduced molecular weight that did not react with antiserum raised against the parental strain. These results show an essential role for the galE gene in the synthesis of C. jejuni LPS. The galE mutant also showed a reduction in its ability to adhere to and invade INT407 cells. However, it was still able to colonize chickens to the same level as the wild-type strain. The serum resistance and hemolytic activity of this mutant were not changed compared to the parent strain. The ability of the mutant to take up DNA and integrate it in its genome was reduced 20-fold. These results show that LPS of C. jejuni is an important virulence factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Gne and GalE in the virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila serotype O34.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jan;189(2):540-50. doi: 10.1128/JB.01260-06. Epub 2006 Nov 10. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17098903 Free PMC article.
-
The lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis locus of Campylobacter jejuni 81116.Microbiology (Reading). 1998 Aug;144 ( Pt 8):2049-2061. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-8-2049. Microbiology (Reading). 1998. PMID: 9720026
-
Brucella melitensis 16M: characterisation of the galE gene and mouse immunisation studies with a galE deficient mutant.Vet Microbiol. 1999 Feb 23;65(1):21-36. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(98)00281-8. Vet Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10068125
-
Polyphosphate and associated enzymes as global regulators of stress response and virulence in Campylobacter jejuni.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep 7;22(33):7402-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7402. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27672264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical and stereochemical actions of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase.Acc Chem Res. 2013 Jul 16;46(7):1417-26. doi: 10.1021/ar300246k. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Acc Chem Res. 2013. PMID: 23339688 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural heterogeneity of terminal glycans in Campylobacter jejuni lipooligosaccharides.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040920. Epub 2012 Jul 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22815868 Free PMC article.
-
The AS87_04050 gene is involved in bacterial lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and pathogenicity of Riemerella anatipestifer.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 10;9(10):e109962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109962. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25303276 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoconjugates play a key role in Campylobacter jejuni Infection: interactions between host and pathogen.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Feb 14;2:9. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00009. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic correlates of extraintestinal infection are linked with changes in cell morphology in Campylobacter jejuni.Microb Genom. 2019 Feb;5(2):e000251. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000251. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Microb Genom. 2019. PMID: 30777818 Free PMC article.
-
Guillain-Barré syndrome, transverse myelitis and infectious diseases.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Jun;15(6):547-562. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.142. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29375121 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Aspinall G O, Lynch C M, Pang H, Shaver R T, Moran A P. Chemical structures of the core region of Campylobacter jejuni O:3 lipopolysaccharide and an associated polysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1995;231:570–578. - PubMed
-
- Aspinall G O, McDonald A G, Pang H, Kurjanczyk L A, Penner J L. Lipopolysaccharides of Campylobacter jejuni serotype O:19: structures of core oligosaccharide regions from the serostrain and two bacterial isolates from patients with the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Biochemistry. 1994;33:241–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

