Distinct protein interaction domains and protein spreading in a complex centromere
- PMID: 10766735
- PMCID: PMC316498
Distinct protein interaction domains and protein spreading in a complex centromere
Abstract
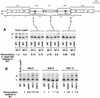
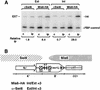
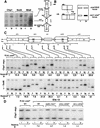
Fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) centromeres are composed of large (40-100 kb) inverted repeats that display heterochromatic features, thus providing a good model for higher eukaryotic centromeres. The association of three proteins that mediate region-specific silencing across centromere 1 has been mapped by quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation. Swi6 and Chp1 are confined to the flanking outer repeats and Swi6 can spread across at least 3 kb of extraneous chromatin in cen1. In contrast, Mis6 coats the inner repeats and central core. tRNA genes demarcate this transition zone. These analyses clearly define two distinct domains within this complex centromere which interact with different proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct centromere domain structures with separate functions demonstrated in live fission yeast cells.J Cell Sci. 2003 Oct 1;116(Pt 19):4035-42. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00707. Epub 2003 Aug 19. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12928332
-
Requirement of heterochromatin for cohesion at centromeres.Science. 2001 Dec 21;294(5551):2539-42. doi: 10.1126/science.1064027. Epub 2001 Oct 11. Science. 2001. PMID: 11598266
-
Recruitment of cohesin to heterochromatic regions by Swi6/HP1 in fission yeast.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;4(1):89-93. doi: 10.1038/ncb739. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11780129
-
Centromere structure and function in budding and fission yeasts.New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):10-9. New Biol. 1990. PMID: 2078550 Review.
-
Studies on the mechanism of RNAi-dependent heterochromatin assembly.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:461-71. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.044. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381328 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel type of silencing factor, Clr2, is necessary for transcriptional silencing at various chromosomal locations in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Aug 18;32(15):4421-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh780. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15317867 Free PMC article.
-
Fta2, an essential fission yeast kinetochore component, interacts closely with the conserved Mal2 protein.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Oct;17(10):4167-78. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-04-0264. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16855021 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved organization of centromeric chromatin in flies and humans.Dev Cell. 2002 Mar;2(3):319-30. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00135-1. Dev Cell. 2002. PMID: 11879637 Free PMC article.
-
Human centromere chromatin protein hMis12, essential for equal segregation, is independent of CENP-A loading pathway.J Cell Biol. 2003 Jan 6;160(1):25-39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200210005. Epub 2003 Jan 6. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12515822 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi hushes heterochromatin.Genome Biol. 2002;3(12):REVIEWS1035. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-12-reviews1035. Epub 2002 Nov 28. Genome Biol. 2002. PMID: 12537580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aagaard L, Laible G, Selenko P, Schmid M, Dorn R, Schotta G, Kuhfittig S, Wolf A, Lebersorger A, Singh PB, et al. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO J. 1999;18:1923–1938. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allshire RC. Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1996. Transcriptional silencing in the fission yeast: A manifestation of higher order chromosome structure and functions; pp. 443–466.
-
- Allshire RC, Javerzat J-P, Redhead NJ, Cranston G. Position effect variegation at fission yeast centromeres. Cell. 1994;76:157–169. - PubMed
-
- Allshire RC, Nimmo ER, Ekwall K, Javerzat J-P, Cranston G. Mutations derepressing silent domains within fission yeast centromeres disrupt chromosome segregation. Genes & Dev. 1995;9:218–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
