HIV-1 gp120 and chemokines activate ion channels in primary macrophages through CCR5 and CXCR4 stimulation
- PMID: 10758170
- PMCID: PMC18318
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.090521697
HIV-1 gp120 and chemokines activate ion channels in primary macrophages through CCR5 and CXCR4 stimulation
Abstract
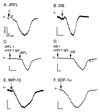
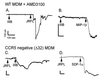
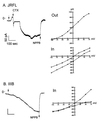
HIV type 1 (HIV-1) uses the chemokine receptors CCR5 and CXCR4 as coreceptors for entry into target cells. Here we show that the HIV-1 envelope gp120 (Env) activates multiple ionic signaling responses in primary human macrophages, which are important targets for HIV-1 in vivo. Env from both CCR5-dependent JRFL (R5) and CXCR4-dependent IIIB (X4) HIV-1 opened calcium-activated potassium (K(Ca)), chloride, and calcium-permeant nonselective cation channels in macrophages. These signals were mediated by CCR5 and CXCR4 because macrophages lacking CCR5 failed to respond to JRFL and an inhibitor of CXCR4 blocked ion current activation by IIIB. MIP-1beta and SDF-1alpha, chemokine ligands for CCR5 and CXCR4, respectively, also activated K(Ca) and Cl(-) currents in macrophages, but nonselective cation channel activation was unique to gp120. Intracellular Ca(2+) levels were also elevated by gp120. The patterns of activation mediated by CCR5 and CXCR4 were qualitatively similar but quantitatively distinct, as R5 Env activated the K(Ca) current more frequently, elicited Cl(-) currents that were approximately 2-fold greater in amplitude, and elevated intracellular Ca(+2) to higher peak and steady-state levels. Env from R5 and X4 primary isolates evoked similar current responses as the corresponding prototype strains. Thus, the interaction of HIV-1 gp120 with CCR5 or CXCR4 evokes complex and distinct signaling responses in primary macrophages, and gp120-evoked signals differ from those activated by the coreceptors' chemokine ligands. Intracellular signaling responses of macrophages to HIV-1 may modulate postentry steps of infection and cell functions apart from infection.
Figures
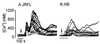
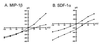
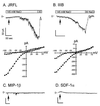
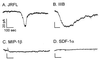
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 gp120 and chemokine activation of Pyk2 and mitogen-activated protein kinases in primary macrophages mediated by calcium-dependent, pertussis toxin-insensitive chemokine receptor signaling.Blood. 2001 Nov 15;98(10):2909-16. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.10.2909. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11698270
-
Chemokine signaling and HIV-1 fusion mediated by macrophage CXCR4: implications for target cell tropism.J Leukoc Biol. 2000 Sep;68(3):318-23. J Leukoc Biol. 2000. PMID: 10985246
-
Macrophage activation through CCR5- and CXCR4-mediated gp120-elicited signaling pathways.J Leukoc Biol. 2003 Nov;74(5):676-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0503206. Epub 2003 Jul 22. J Leukoc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12960231 Review.
-
gp120 envelope glycoproteins of human immunodeficiency viruses competitively antagonize signaling by coreceptors CXCR4 and CCR5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jul 7;95(14):8005-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8005. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9653130 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine receptor utilization and macrophage signaling by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120: Implications for neuropathogenesis.J Neurovirol. 2004;10 Suppl 1:91-6. doi: 10.1080/753312758. J Neurovirol. 2004. PMID: 14982745 Review.
Cited by
-
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein blocks HIV-1 infection in primary human macrophages.Virus Res. 2007 Feb;123(2):178-89. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.09.004. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Virus Res. 2007. PMID: 17030448 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between HIV-1 gp120, chemokines, and cultured adult microglial cells.J Neurovirol. 2001 Jun;7(3):196-207. doi: 10.1080/13550280152403245. J Neurovirol. 2001. PMID: 11517394
-
Receptors and entry cofactors for retroviruses include single and multiple transmembrane-spanning proteins as well as newly described glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored and secreted proteins.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001 Sep;65(3):371-89, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.3.371-389.2001. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11528001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The macrophage response to HIV-1: Intracellular control of X4 virus replication accompanied by activation of chemokine and cytokine synthesis.J Neurovirol. 2002 Dec;8(6):599-610. doi: 10.1080/13550280290100923. J Neurovirol. 2002. PMID: 12476353 Review.
-
Induction of the Galpha(q) signaling cascade by the human immunodeficiency virus envelope is required for virus entry.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(18):9191-205. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00424-08. Epub 2008 Jul 16. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18632858 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

