Compatible-solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions
- PMID: 10742244
- PMCID: PMC92025
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.4.1572-1579.2000
Compatible-solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions
Abstract
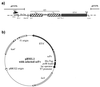
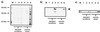
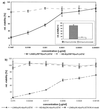
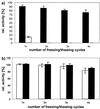
The standard method of producing recombinant proteins such as immunotoxins (rITs) in large quantities is to transform gram-negative bacteria and subsequently recover the desired protein from inclusion bodies by intensive de- and renaturing procedures. The major disadvantage of this technique is the low yield of active protein. Here we report the development of a novel strategy for the expression of functional rIT directed to the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli. rITs were recovered by freeze-thawing of pellets from shaking cultures of bacteria grown under osmotic stress (4% NaCl plus 0.5 M sorbitol) in the presence of compatible solutes. Compatible solutes, such as glycine betaine and hydroxyectoine, are low-molecular-weight osmolytes that occur naturally in halophilic bacteria and are known to protect proteins at high salt concentrations. Adding 10 mM glycine betaine for the cultivation of E. coli under osmotic stress not only allowed the bacteria to grow under these otherwise inhibitory conditions but also produced a periplasmic microenvironment for the generation of high concentrations of correctly folded rITs. Protein purified by combinations of metal ion affinity and size exclusion chromatography was substantially stabilized in the presence of 1 M hydroxyecotine after several rounds of freeze-thawing, even at very low protein concentrations. The binding properties and cytotoxic potency of the rITs were confirmed by competitive experiments. This novel compatible-solute-guided expression and purification strategy might also be applicable for high-yield periplasmic production of recombinant proteins in different expression systems.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human angiogenin fused to human CD30 ligand (Ang-CD30L) exhibits specific cytotoxicity against CD30-positive lymphoma.Cancer Res. 2001 Dec 15;61(24):8737-42. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11751393
-
Periplasmic targeting of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;390:47-61. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-466-7_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951680
-
Marinococcus halophilus DSM 20408T encodes two transporters for compatible solutes belonging to the betaine-carnitine-choline transporter family: identification and characterization of ectoine transporter EctM and glycine betaine transporter BetM.Extremophiles. 2004 Jun;8(3):175-84. doi: 10.1007/s00792-004-0375-6. Epub 2004 Feb 11. Extremophiles. 2004. PMID: 14872322
-
Purification of secreted recombinant proteins from Escherichia coli.Bioprocess Technol. 1991;12:163-81. Bioprocess Technol. 1991. PMID: 1367083 Review.
-
Periplasmic chaperones used to enhance functional secretion of proteins in E. coli.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;705:211-24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61737-967-3_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21125388 Review.
Cited by
-
Refolding and simultaneous purification by three-phase partitioning of recombinant proteins from inclusion bodies.Protein Sci. 2008 Nov;17(11):1987-97. doi: 10.1110/ps.036939.108. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Protein Sci. 2008. PMID: 18780821 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of the β-selectivity of a bacterial aminotransferase.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28495-502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375238. Epub 2012 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22745123 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of dry protein coatings with compatible solutes.Biointerphases. 2018 Jun 29;13(6):06E401. doi: 10.1116/1.5031189. Biointerphases. 2018. PMID: 29958498 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in the production of the human recombinant enzyme N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (rhGALNS) in Escherichia coli using synthetic biology approaches.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 19;7(1):5844. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06367-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28724898 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2009 May 14;8:26. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-8-26. Microb Cell Fact. 2009. PMID: 19442264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altamiro M M, Garcia C, Possani L D, Fersht A R. Oxidative refolding chromatography: folding of the scorpion toxin Cn5. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17:187–191. - PubMed
-
- Baneyx F, Georgiou G. Degradation of secreted proteins in Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;665:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Barth S, Huhn M, Wels W, Diehl V, Engert A. Construction and in vitro evaluation of RFT5(scFv)-ETA′, a new recombinant single-chain immunotoxin with specific cytotoxicity toward CD25+ Hodgkin-derived cell lines. Int J Mol Med. 1998;1:249–256. - PubMed
-
- Barth S, Matthey B, Huhn M, Diehl V, Engert A. CD30L-ETA′: a new recombinant immunotoxin based on the CD30 ligand for possible use against human lymphoma. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1999;5:69–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

