NMDA receptor content of synapses in stratum radiatum of the hippocampal CA1 area
- PMID: 10729331
- PMCID: PMC6772245
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-07-02512.2000
NMDA receptor content of synapses in stratum radiatum of the hippocampal CA1 area
Abstract
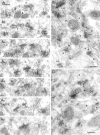
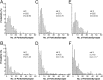
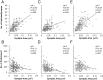
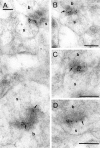
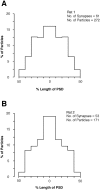
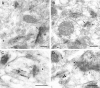
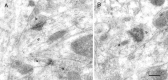
Glutamate receptors activated by NMDA (NMDARs) or AMPA (AMPARs) are clustered on dendritic spines of pyramidal cells. Both the AMPAR-mediated postsynaptic responses and the synaptic AMPAR immunoreactivity show a large intersynapse variability. Postsynaptic responses mediated by NMDARs show less variability. To assess the variability in NMDAR content and the extent of their coexistence with AMPARs in Schaffer collateral-commissural synapses of adult rat CA1 pyramidal cells, electron microscopic immunogold localization of receptors has been used. Immunoreactivity of NMDARs was detected in virtually all synapses on spines, but AMPARs were undetectable, on average, in 12% of synapses. A proportion of synapses had a very high AMPAR content relative to the mean content, resulting in a distribution more skewed toward larger values than that of NMDARs. The variability of synaptic NMDAR content [coefficient of variation (CV), 0.64-0.70] was much lower than that of the AMPAR content (CV, 1.17-1.45). Unlike the AMPAR content, the NMDAR content showed only a weak correlation with synapse size. As reported previously for AMPARs, the immunoreactivity of NMDARs was also associated with the spine apparatus within spines. The results demonstrate that the majority of the synapses made by CA3 pyramidal cells onto spines of CA1 pyramids express both NMDARs and AMPARs, but with variable ratios. A less-variable NMDAR content is accompanied by a wide variability of AMPAR content, indicating that the regulation of expression of the two receptors is not closely linked. These findings support reports that fast excitatory transmission at some of these synapses is mediated by activation mainly of NMDARs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences in the expression of AMPA and NMDA receptors between axospinous perforated and nonperforated synapses are related to the configuration and size of postsynaptic densities.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Jan 1;468(1):86-95. doi: 10.1002/cne.10950. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14648692
-
Large variability in synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor density on interneurons and a comparison with pyramidal-cell spines in the rat hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2003;119(2):347-63. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00157-x. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12770551
-
TARP γ-2 and γ-8 Differentially Control AMPAR Density Across Schaffer Collateral/Commissural Synapses in the Hippocampal CA1 Area.J Neurosci. 2016 Apr 13;36(15):4296-312. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4178-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27076426 Free PMC article.
-
Making of a Synapse: Recurrent Roles of Drebrin A at Excitatory Synapses Throughout Life.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1006:119-139. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-56550-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28865018 Review.
-
Regulation of AMPA receptor recruitment at developing synapses.Trends Neurosci. 2008 Feb;31(2):82-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.11.010. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Trends Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18201773 Review.
Cited by
-
Microdomains in forebrain spines: an ultrastructural perspective.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Feb;47(1):77-89. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8345-y. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 22983912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors occur at postsynaptic densities of AMPA receptor-positive and -negative excitatory synapses in rat sensory cortex.J Neurosci. 2002 Jun 15;22(12):5001-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-12-05001.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12077196 Free PMC article.
-
Clusters of interacting receptors can stabilize synaptic efficacies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 4;102(40):14440-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506934102. Epub 2005 Sep 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16189022 Free PMC article.
-
Laminar organization of the NMDA receptor complex within the postsynaptic density.J Neurosci. 2001 Feb 15;21(4):1211-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01211.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160391 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired synaptic scaling in mouse hippocampal neurones expressing NMDA receptors with reduced calcium permeability.J Physiol. 2005 Feb 1;562(Pt 3):771-83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.076794. Epub 2004 Dec 2. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15576450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JDB, Mulvihill E, McIlhinney RAJ, Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1α) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993;11:771–787. - PubMed
-
- Bernard V, Bolam JP. Subcellular and subsynaptic distribution of the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptor in the neostriatum and globus pallidus of the rat: co-localization at synapses with the GluR2/3 subunit of the AMPA receptor. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:3721–3736. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron. 1998;21:13–26. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
