Identification and characterization of a shared TNFR-related receptor for subgroup B, D, and E avian leukosis viruses reveal cysteine residues required specifically for subgroup E viral entry
- PMID: 10729132
- PMCID: PMC111866
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.8.3572-3578.2000
Identification and characterization of a shared TNFR-related receptor for subgroup B, D, and E avian leukosis viruses reveal cysteine residues required specifically for subgroup E viral entry
Abstract
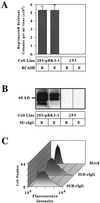
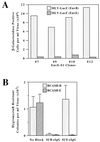
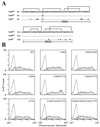
Genetic and receptor interference data have indicated the presence of one or more cellular receptors for subgroup B, D, and E avian leukosis viruses (ALV) encoded by the s1 allele of the chicken tvb locus. Despite the prediction that these viruses use the same receptor, they exhibit a nonreciprocal receptor interference pattern: ALV-B and ALV-D can interfere with infection by all three viral subgroups, but ALV-E only interferes with infection by subgroup E viruses. We identified a tvb(s1) cDNA clone which encodes a tumor necrosis factor receptor-related receptor for ALV-B, -D, and -E. The nonreciprocal receptor interference pattern was reconstituted in transfected human 293 cells by coexpressing the cloned receptor with the envelope (Env) proteins of either ALV-B or ALV-E. This pattern of interference was also observed when soluble ALV surface (SU)-immunoglobulin fusion proteins were bound to this cellular receptor before viral challenge. These data demonstrate that viral Env-receptor interactions can account for the nonreciprocal interference between ALV subgroups B, D, and E. Furthermore, they indicate that a single chicken gene located at tvb(s1) encodes receptors for these three viral subgroups. The TVB(S1) protein differs exclusively at residue 62 from the published subgroup B- and D-specific receptor, encoded by the s3 allele of tvb. Residue 62 is a cysteine in TVB(S1) but is a serine in TVB(S3), giving TVB(S1) an even number of cysteines in the extracellular domain. We present evidence for a disulfide bond requirement in TVB(S1) for ALV-E infection but not for ALV-B infection. Thus, ALV-B and ALV-E interact in fundamentally different ways with this shared receptor, a finding that may account for the observed biological differences between these two ALV subgroups.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TVB receptors for cytopathic and noncytopathic subgroups of avian leukosis viruses are functional death receptors.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(24):11490-4. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.24.11490-11494.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11090145 Free PMC article.
-
Two functionally distinct forms of a retroviral receptor explain the nonreciprocal receptor interference among subgroups B, D, and E avian leukosis viruses.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3520-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3520-3526.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264341 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Occurring Frameshift Mutations in the tvb Receptor Gene Are Responsible for Decreased Susceptibility of Chicken to Infection with Avian Leukosis Virus Subgroups B, D, and E.J Virol. 2018 Mar 28;92(8):e01770-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01770-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29263268 Free PMC article.
-
An NF-kappa B-dependent survival pathway protects against cell death induced by TVB receptors for avian leukosis viruses.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(11):5581-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5581-5587.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11991986 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a cellular receptor for subgroup E avian leukosis virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Oct 14;94(21):11617-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.21.11617. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9326659 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A single-amino-acid substitution in the TvbS1 receptor results in decreased susceptibility to infection by avian sarcoma and leukosis virus subgroups B and D and resistance to infection by subgroup E in vitro and in vivo.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(5):2097-105. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02206-07. Epub 2007 Dec 19. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18094190 Free PMC article.
-
TVB receptors for cytopathic and noncytopathic subgroups of avian leukosis viruses are functional death receptors.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(24):11490-4. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.24.11490-11494.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11090145 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient subgroup C avian sarcoma and leukosis virus receptor activity requires the IgV domain of the Tvc receptor and proper display on the cell membrane.J Virol. 2008 Nov;82(22):11419-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01408-08. Epub 2008 Sep 3. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18768966 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in Both the Surface and Transmembrane Envelope Glycoproteins of the RAV-2 Subgroup B Avian Sarcoma and Leukosis Virus Are Required to Escape the Antiviral Effect of a Secreted Form of the TvbS3 Receptor †.Viruses. 2019 May 31;11(6):500. doi: 10.3390/v11060500. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31159208 Free PMC article.
-
Library screening and receptor-directed targeting of gammaretroviral vectors.Future Microbiol. 2013 Jan;8(1):107-21. doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.122. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23252496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bacon L D, Smith E J, Fadly A M, Crittenden L B. Development of an alloantiserum (R2) that detects susceptibility of chickens to subgroup E endogenous avian leukosis virus. Avian Pathol. 1996;25:551–568. - PubMed
-
- Banner D W, D'Arcy A, Janes W, Gentz R, Schoenfeld H J, Broger C, Loetscher H, Lesslauer W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell. 1993;73:431–445. - PubMed
-
- Bates P, Young J A, Varmus H E. A receptor for subgroup A Rous sarcoma virus is related to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Cell. 1993;74:1043–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

